Stress Marks on the Genome: Use or Lose?
- PMID: 30654540
- PMCID: PMC6358951
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020364
Stress Marks on the Genome: Use or Lose?
Abstract
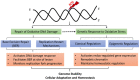
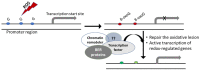
Oxidative stress and the resulting damage to DNA are inevitable consequence of endogenous physiological processes further amplified by cellular responses to environmental exposures. If left unrepaired, oxidative DNA lesions can block essential processes such as transcription and replication or can induce mutations. Emerging data also indicate that oxidative base modifications such as 8-oxoG in gene promoters may serve as epigenetic marks, and/or provide a platform for coordination of the initial steps of DNA repair and the assembly of the transcriptional machinery to launch adequate gene expression alterations. Here, we briefly review the current understanding of oxidative lesions in genome stability maintenance and regulation of basal and inducible transcription.
Keywords: 8-oxoG; DNA damage; DNA repair; epigenetic; gene expression; helicase; oxidative stress; replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

