Potent Cytotoxic Analogs of Amphidinolides from the Atlantic Octocoral Stragulum bicolor
- PMID: 30654557
- PMCID: PMC6356882
- DOI: 10.3390/md17010058
Potent Cytotoxic Analogs of Amphidinolides from the Atlantic Octocoral Stragulum bicolor
Abstract
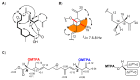
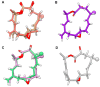
Amphidinolides are cytotoxic macrolides produced by symbiotic unicellular microalgae of the genus Amphidinium. Here we describe the identification of four related molecules belonging to this macrolide family isolated from the invertebrate Stragulum bicolor. The new molecules, named amphidinolide PX1-PX3 and stragulin A (1⁻4), show an unprecedented carbon skeleton whose complete stereochemistry has been determined by spectroscopic and computational methods. Differences in the structures of these molecules modulate their biological activity in a panel of tumor cell lines, but the opened derivative stragulin (4) shows a very potent and specific cytotoxic activity (IC50 0.18 µM) against the aggressive human melanoma cell A2058.
Keywords: Stragulum bicolor; amphidinolides; cytotoxic macrolides; stereochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kobayashi J., Ishibachi M. Bioactive Metabolites of Symbiotic Marine Microorganisms. Chem. Rev. 1993;93:1753–1769. doi: 10.1021/cr00021a005. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

