Tocotrienols Modulate a Life or Death Decision in Cancers
- PMID: 30654580
- PMCID: PMC6359475
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020372
Tocotrienols Modulate a Life or Death Decision in Cancers
Abstract
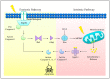
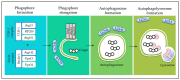
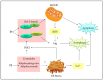
Malignancy often arises from sophisticated defects in the intricate molecular mechanisms of cells, rendering a complicated molecular ground to effectively target cancers. Resistance toward cell death and enhancement of cell survival are the common adaptations in cancer due to its infinite proliferative capacity. Existing cancer treatment strategies that target a single molecular pathway or cancer hallmark fail to fully resolve the problem. Hence, multitargeted anticancer agents that can concurrently target cell death and survival pathways are seen as a promising alternative to treat cancer. Tocotrienols, a minor constituent of the vitamin E family that have previously been reported to induce various cell death mechanisms and target several key survival pathways, could be an effective anticancer agent. This review puts forward the potential application of tocotrienols as an anticancer treatment from a perspective of influencing the life or death decision of cancer cells. The cell death mechanisms elicited by tocotrienols, particularly apoptosis and autophagy, are highlighted. The influences of several cell survival signaling pathways in shaping cancer cell death, particularly NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and Wnt, are also reviewed. This review may stimulate further mechanistic researches and foster clinical applications of tocotrienols via rational drug designs.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; cancer; cell death; cell survival; tocotrienols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Natural forms of vitamin E and metabolites-regulation of cancer cell death and underlying mechanisms.IUBMB Life. 2019 Apr;71(4):495-506. doi: 10.1002/iub.1978. Epub 2018 Dec 11. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 30548200 Review.
-
Tocotrienols induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines via an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent increase in extrinsic death receptor signaling.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Nov;124(2):361-75. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0786-2. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 20157774
-
Tocotrienols induce apoptosis and autophagy in rat pancreatic stellate cells through the mitochondrial death pathway.Gastroenterology. 2007 Jun;132(7):2518-32. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.107. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17570223
-
Tocotrienols: balancing the mitochondrial crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy.Autophagy. 2007 Nov-Dec;3(6):652-4. doi: 10.4161/auto.5088. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17932465
-
Tocotrienols target PI3K/Akt signaling in anti-breast cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Sep;13(7):1039-47. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990116. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23272909 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinically Relevant Genes and Proteins Modulated by Tocotrienols in Human Colon Cancer Cell Lines: Systematic Scoping Review.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 12;13(11):4056. doi: 10.3390/nu13114056. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836311 Free PMC article.
-
Tocotrienols reach the brain and play roles in the attenuation of body weight gain and improvement of cognitive function in high-fat diet-treated mice.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2021 Nov;69(3):256-264. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.21-10. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34857987 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Activity of Delta-Tocotrienol in Human Hepatocarcinoma: Involvement of Autophagy Induction.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;16(15):2654. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152654. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123382 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the curative effects of palm vitamin E tocotrienols on autoimmune arthritis disease in vivo.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 14;9(1):16793. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53424-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31727971 Free PMC article.
-
The synergism of Clinacanthus nutans Lindau extracts with gemcitabine: downregulation of anti-apoptotic markers in squamous pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Sep 14;19(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2663-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31521140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Cancer Statistics-National Cancer Institute. [(accessed on 18 December 2018)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/statistics.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

