Nature of selection varies on different domains of IFI16-like PYHIN genes in ruminants
- PMID: 30654734
- PMCID: PMC6335826
- DOI: 10.1186/s12862-018-1334-7
Nature of selection varies on different domains of IFI16-like PYHIN genes in ruminants
Abstract
Background: ALRs (AIM2-like Receptors) are germline encoded PRRs that belong to PYHIN gene family of cytokines, which are having signature N-terminal PYD (Pyrin, PAAD or DAPIN) domain and C-terminal HIN-200 (hematopoietic, interferon-inducible nuclear protein with 200 amino acid repeat) domain joined by a linker region. The positively charged HIN-200 domain senses and binds with negatively charged phosphate groups of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) purely through electrostatic attractions. On the other hand, PYD domain interacts homotypically with a PYD domain of other mediators to pass the signals to effector molecules downwards the pathways for inflammatory responses. There is remarkable inter-specific diversity in the numbers of functional PYHIN genes e.g. one in cow, five in human, thirteen in mice etc., while there is a unique loss of PYHIN genes in the bat genomes which was revealed by Ahn et al. (2016) by studying genomes of ten different bat species belonging to sub-orders yinpterochiroptera and yangochiroptera. The conflicts between host and pathogen interfaces are compared with "Red queen's arms race" which is also described as binding seeking dynamics and binding avoidance dynamics. As a result of this never-ending rivalry, eukaryotes developed PRRs as antiviral mechanism while viruses developed counter mechanisms to evade host immune defense. The PYHIN receptors are directly engaged with pathogenic molecules, so these should have evolved under the influence of selection pressures. In the current study, we investigated the nature of selection pressure on different domain types of IFI16-like (IFI16-L) PYHIN genes in ruminants.
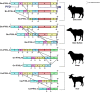
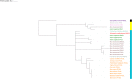
Results: Three transcript variants of the IFI16-like gene were found in PBMCs of ruminant animals-water buffalo, zebu cattle, goat, and sheep. The IFI16-like gene has one N-terminal PYD domain and one C-terminal HIN-200 domain, separated by an inter-domain linker region. HIN domain and inter-domain region are positively selected while the PYD domain is under the influence of purifying selection.
Conclusion: Herein, we conclude that the nature of selection pressure varies on different parts (PYD domain, HIN domain, and inter-domain linker region) of IFI16-like PYHIN genes in the ruminants. This data can be useful to predict the molecular determinants of pathogen interactions.
Keywords: DAMP; HIN; IFI16; IFI16-like; Inter-domain; PAMP; PRR; PYD; PYHIN; Selection.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No animal was slaughtered for this research. Blood samples were collected from institutional (NDRI) animal herd with consent of the institute ethical committee in the presence of Veterinary Doctor.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Janeway CA., Jr Pillars article: approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold spring harb symp quant biol. 1989. 54: 1-13. J Immunol. 2013;191(9):4475–4487. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi ME. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 2014;157(5):1013–1022. - PubMed
-
- Connolly DJ, Bowie AG. The emerging role of human PYHIN proteins in innate immunity: implications for health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;92(3):405–414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

