Programmes for the prevention of mother-to-child HIV infection transmission have made progress in Yunnan Province, China, from 2006 to 2015: a cost effective and cost-benefit evaluation
- PMID: 30654744
- PMCID: PMC6337853
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-3708-x
Programmes for the prevention of mother-to-child HIV infection transmission have made progress in Yunnan Province, China, from 2006 to 2015: a cost effective and cost-benefit evaluation
Abstract
Background: Prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) of HIV programmes have substantially reduced HIV infections among infants in Yunnan Province, China. We conducted a macro-level economic evaluation of Yunnan's PMTCT programmes over the 10 years from 2006 to 2015 from a policymaker perspective.
Methods: The study methodology was in accordance with the guidelines from the Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS) statement. We quantified the output from the Yunnan's PMTCT programmes by estimating the number of paediatric HIV infections averted and the relative savings to both the health care system and society. The return-on-investment ratio (ROI) was calculated as the output (numerator) divided by the input (denominator).
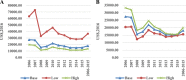
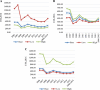
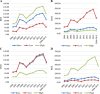
Results: We have found that the US$ 49 million investment in Yunnan's PMTCT programmes over the period from 2006 to 2015 averted an estimated 2725 new paediatric HIV infections and resulted in an estimated 134,008 QALY acquired. It saved an estimated US$ 0.5 billion in treatment expenditures for Yunnan's healthcare system and nearly US$ 3.9 billion in productivity. The ROI was 88.4, meaning every US$ 1 invested brought about US$ 88.4 in benefits.
Conclusions: Our results support the ongoing investment in PMTCT programmes in Yunnan Province. The PMTCT strategy is a cost effective and cost-benefit strategy in the periods from 2006 to 2015. Despite higher investments in the future, the overall investment in the PMTCT programmes in Yunnan province could be offset by averting more paediatric infections.
Keywords: Cost benefit; Cost effective; Economic evaluation; Prevention mother-to-child transmission of HIV; Yunnan Province.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Because the study was based on aggregate data, ethical approval was not required. All data used in this study were obtained through approvals from Yunnan AIDS Prevention Bureau.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of option B+ in prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV in Yunnan Province, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 11;19(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-3976-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31185927 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of nevirapine to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission in eight African countries.AIDS. 2004 Aug 20;18(12):1661-71. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000131353.06784.8f. AIDS. 2004. PMID: 15280777
-
Return on Investment From Expenditures Incurred to Eliminate Mother-To-Child Transmission Among HIV-Infected Women in New York State: 1998-2013.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2016 Apr 15;71(5):558-62. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000899. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2016. PMID: 26974414
-
Option B+ for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection in developing countries: a review of published cost-effectiveness analyses.Health Policy Plan. 2016 Oct;31(8):1133-41. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czw025. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Health Policy Plan. 2016. PMID: 27016949 Review.
-
Evidence on the cost-effectiveness of lifelong antiretroviral therapy for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV: implications for resource-limited countries in sub-Saharan Africa.Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2017 Oct;17(5):459-467. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2017.1364161. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2017. PMID: 28770641 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of ART on Stillbirth and Neonatal Death Among HIV-positive Pregnant Women - Yunnan Province, China, 2013-2022.China CDC Wkly. 2025 Feb 21;7(8):265-270. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2025.042. China CDC Wkly. 2025. PMID: 40104519 Free PMC article.
-
Projected impact of fast-tracking of anti-retroviral treatment coverage on vertical transmission of HIV in India.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Sep 18;4(9):e0003702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0003702. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39292653 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.Infect Dis Poverty. 2022 Jun 15;11(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40249-022-00983-z. Infect Dis Poverty. 2022. PMID: 35706049 Free PMC article.
-
Fertility desire among HIV-positive individuals in the Chinese sociocultural context: A qualitative study.J Educ Health Promot. 2023 May 31;12:156. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_126_23. eCollection 2023. J Educ Health Promot. 2023. PMID: 37404936 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluations of training and education interventions for improved infectious disease management in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic literature review.BMJ Open. 2022 Feb 21;12(2):e053832. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053832. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35190429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y. The process of prevention of mother-to-child transmission of AIDS. Journal of Kunming Medical University. 2012;11:1–3.
-
- Dai R, Feng J, Tang MZ, et al. Mother-to-child transmission rate of HIV and use of drugs to prevent the transmission in China: a systematic reviewer. Acad J Second Mil Univ. 2014;35:1094–1102. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1008.2014.01094. - DOI
-
- www.gov.cn. Yunnan: the epidemic of HIV was totally stable in Yunnan Province in 2016. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-11/30/content_5140127.htm. 2016–11–30/2016-12-28.
-
- Yunnan Provincial Bureau of Statistics. The Statistical Yearbook of Yunnan Province in 2017. http://www.stats.yn.gov.cn/tjsj/tjnj/201810/t20181030_809120.htm.2018-10....
-
- Zhu XX, Wang XT. The analysis of experimental works in prevention mother-to-child transmission of HIV in Yunnan Province. Maternal & Child Health Care of China. 2005;12:1430–1431.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

