Carbon dioxide de-airing in minimal invasive cardiac surgery, a new effective device
- PMID: 30654802
- PMCID: PMC6337843
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-018-0824-4
Carbon dioxide de-airing in minimal invasive cardiac surgery, a new effective device
Abstract
Background: Arterial air embolism during open heart surgery may cause postoperative complications including cerebral injury, myocardial dysfunction, and dysrhythmias. Despite standard de-airing techniques during surgery large amounts of arterial air emboli may still occur, especially during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass. To prevent this insufflation of carbon dioxide in the wound cavity has been used since the 1950s. The aim of this study was to assess a new mini-diffuser for efficient carbon dioxide de-airing of a minimal invasive cardiothoracic wound cavity model. Up until now no device has been evaluated for this purpose.
Methods: A new insufflation device, a mini-diffuser, was tested. A thin plastic tube was used as control. The end of the mini-diffuser or the control, respectively, was positioned in a minimal invasive thoracic wound model. Remaining air content was measured during steady state and during intermittent suction with a rough suction device at different carbon dioxide flow rates. Measurements were also carried out in the open surgical wound during minimal invasive aortic surgery in six patients.
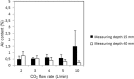
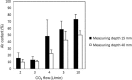
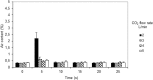
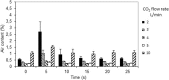
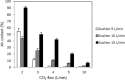
Results: The air content was below 1% 4 cm below the surface of the open wound model during continuous carbon dioxide inflow of 2-10 L/min with the mini diffuser. In comparison, carbon dioxide insufflation via the open-ended tube resulted in a mean air content between 10 and 75%. The mean air content of the wound model remained below 1% at a carbon dioxide flow rate of 3-5 L/min during intermittent application of a suction device with a suction rate of 15 L/min. In 6 patients undergoing minimal invasive aortic valve replacement air content in the open surgical wound remained below 1% at a continuous carbon dioxide flow rate of 5 and 8 L/min via the mini-diffuser, respectively.
Conclusions: The mini diffuser was effective for carbon dioxide de-airing, i.e. < 1% remaining air, of a minimal invasive cardiothoracic wound cavity model with and without intermittent rough suction as well as in patients undergoing minimal invasive aortic valve surgery.
Keywords: Carbon dioxide; Emboli; Minimal invasive cardiac surgery; de-airing.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical Approval is obtained from the Regional ethics comity of Stockholm 2015/323–32. Informed consent to participate in the study was given by the participating patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
JvdL and PS are shareholders of the company that manufactures the mini-diffuser and JvdL is a member of the company board.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Eguchi S, Sakurai Y, Yamaguchi A. The use of carbon dioxide gas to prevent air embolism during open heart surgery. Acta Med Biol. 1963;11:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Goldfarb D, Bahnson HT. Early and late effects on the heart of small amounts of air in the coronary circulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1963;46:368–378. - PubMed
-
- Spencer FC, Rossi NP, Yu S-C, Koepke JA. The significance of air embolism during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1965;49:615–634. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

