Desmoglein 1 Regulates Invadopodia by Suppressing EGFR/Erk Signaling in an Erbin-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 30655320
- PMCID: PMC6581214
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0048
Desmoglein 1 Regulates Invadopodia by Suppressing EGFR/Erk Signaling in an Erbin-Dependent Manner
Abstract
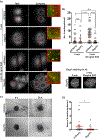
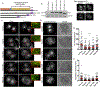
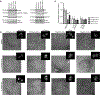
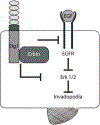
Loss of the desmosomal cell-cell adhesion molecule, Desmoglein 1 (Dsg1), has been reported as an indicator of poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). It has been well established that EGFR signaling promotes the formation of invadopodia, actin-based protrusions formed by cancer cells to facilitate invasion and metastasis, by activating pathways leading to actin polymerization and ultimately matrix degradation. We previously showed that Dsg1 downregulates EGFR/Erk signaling by interacting with the ErbB2-binding protein Erbin (ErbB2 Interacting Protein) to promote keratinocyte differentiation. Here, we provide evidence that restoring Dsg1 expression in cells derived from HNSCC suppresses invasion by decreasing the number of invadopodia and matrix degradation. Moreover, Dsg1 requires Erbin to downregulate EGFR/Erk signaling and to fully suppress invadopodia formation. Our findings indicate a novel role for Dsg1 in the regulation of invadopodia signaling and provide potential new targets for development of therapies to prevent invadopodia formation and therefore cancer invasion and metastasis. IMPLICATIONS: Our work exposes a new pathway by which a desmosomal cadherin called Dsg1, which is lost early in head and neck cancer progression, suppresses cancer cell invadopodia formation by scaffolding ErbB2 Interacting Protein and consequent attenuation of EGF/Erk signaling.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Marur S, and Forastiere AA. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Update on Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc 2016; 91, 386–396. - PubMed
-
- Curry JM, Sprandio J, Cognetti D, Luginbuhl A, Bar-ad V, Pribitkin E, et al. Tumor Microenvironment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Semin. Oncol 2014; 41, 217–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

