Genetic associations with suicide attempt severity and genetic overlap with major depression
- PMID: 30655502
- PMCID: PMC6336846
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-018-0340-2
Genetic associations with suicide attempt severity and genetic overlap with major depression
Abstract
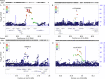
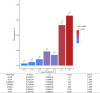
In 2015, ~800,000 people died by suicide worldwide. For every death by suicide there are as many as 25 suicide attempts, which can result in serious injury even when not fatal. Despite this large impact on morbidity and mortality, the genetic influences on suicide attempt are poorly understood. We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of severity of suicide attempts to investigate genetic influences. A discovery GWAS was performed in Yale-Penn sample cohorts of European Americans (EAs, n = 2,439) and African Americans (AAs, n = 3,881). We found one genome-wide significant (GWS) signal in EAs near the gene LDHB (rs1677091, p = 1.07 × 10-8) and three GWS associations in AAs: ARNTL2 on chromosome 12 (rs683813, p = 2.07 × 10-8), FAH on chromosome 15 (rs72740082, p = 2.36 × 10-8), and on chromosome 18 (rs11876255, p = 4.61 × 10-8) in the Yale-Penn discovery sample. We conducted a limited replication analysis in the completely independent Army-STARRS cohorts. rs1677091 replicated in Latinos (LAT, p = 6.52 × 10-3). A variant in LD with FAH rs72740082 (rs72740088; r2 = 0.68) was replicated in AAs (STARRS AA p = 5.23 × 10-3; AA meta, 1.51 × 10-9). When combined for a trans-population meta-analysis, the final sample size included n = 20,153 individuals. Finally, we found significant genetic overlap with major depressive disorder (MDD) using polygenic risk scores from a large GWAS (r2 = 0.007, p = 6.42 × 10-5). To our knowledge, this is the first GWAS of suicide attempt severity. We identified GWS associations near genes involved in anaerobic energy production (LDHB), circadian clock regulation (ARNTL2), and catabolism of tyrosine (FAH). These findings provide evidence of genetic risk factors for suicide attempt severity, providing new information regarding the molecular mechanisms involved.
Conflict of interest statement
J.W.S. is an unpaid member of the Scientific Advisory Board of PsyBrain Inc. and the Bipolar/Depression Research Community Advisory Panel of 23andMe. H.R.K. has been an advisory board member, consultant, or continuing medical education speaker for Indivior, Lundbeck, and Otsuka. He is a member of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology’s Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which was sponsored in the past 3 years by AbbVie, Alkermes, Amygdala Neurosciences, Arbor Pharmaceuticals, Ethypharm, Indivior, Lilly, Lundbeck, Otsuka, and Pfizer. H.R.K. and J.G. are named as inventors on PCT patent application #15/878,640 entitled: “Genotype-guided dosing of opioid agonists,” filed January 24, 2018. R.C.K. received support for his epidemiological studies from Sanofi Aventis; was a consultant for Johnson & Johnson Wellness and Prevention, Sage Pharmaceuticals, Shire, Takeda; and served on an advisory board for the Johnson & Johnson Services Inc. Lake Nona Life Project. R.C.K is a co-owner of DataStat, Inc., a market research firm that carries out healthcare research. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

