Novel role of microRNA-126 in digestive system cancers: From bench to bedside
- PMID: 30655735
- PMCID: PMC6313097
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9639
Novel role of microRNA-126 in digestive system cancers: From bench to bedside
Abstract
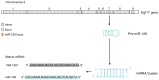
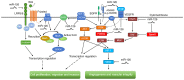
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are ubiquitously expressed, small, non-coding RNAs that regulate the expression of approximately 30% of the human genes at the post-transcriptional level. miRNAs have emerged as crucial modulators in the initiation and progression of various diseases, including numerous cancer types. The high incidence rate of cancer and the large number of cancer-associated cases of mortality are mostly due to a lack of effective treatments and biomarkers for early diagnosis. Therefore there is an urgent requirement to further understand the underlying mechanisms of tumorigenesis. MicroRNA-126 (miR-126) is significantly downregulated in a number of tumor types and is commonly identified as a tumor suppressor in digestive system cancers (DSCs). miR-126 downregulates various oncogenes, including disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 9, v-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog and phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 2. These genes are involved in a number of tumor-associated signaling pathways, including angiogenesis, epithelial-mensenchymal transition and metastasis pathways. The aim of the current review was to summarize the role of miR-126 in DSCs, in terms of its dysregulation, target genes and associated signaling pathways. In addition, the current review has discussed the potential clinical application of miR-126 as a biomarker and therapeutic target for DSCs.
Keywords: clinical applications; digestive system cancers; microRNA-126; signaling pathways; target genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-221: biogenesis, function and signatures in human cancers.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(10):3094-3117. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_15069. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29863255 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MicroRNA-381-A Key Transcriptional Regulator: Its Biological Function and Clinical Application Prospects in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 26;10:535665. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.535665. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33324542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-27a (miR-27a) in Solid Tumors: A Review Based on Mechanisms and Clinical Observations.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 12;9:893. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00893. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31572683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relevance function of microRNA-708 in the pathogenesis of cancer.Cell Signal. 2019 Nov;63:109390. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109390. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Cell Signal. 2019. PMID: 31419576 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value and clinical significance of circulating miR-650 and CA211 in detecting of gastric carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):254. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12117. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32994817 Free PMC article.
-
Underexpression of miR-126-3p in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Feb 1;22(2):573-579. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.2.573. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33639676 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-21 Regulates Stemness in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 24;23(3):1275. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031275. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163198 Free PMC article.
-
Nickel's Role in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Potential Involvement of microRNAs.Toxics. 2022 Mar 21;10(3):148. doi: 10.3390/toxics10030148. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35324773 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs Orchestrate Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis: Advances in Therapy.Mol Cancer. 2020 Feb 15;19(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1140-x. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32059676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
