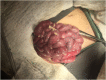
Spontaneous pneumococcal peritonitis diagnosed by qPCR
- PMID: 30656139
- PMCID: PMC6327877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00489
Spontaneous pneumococcal peritonitis diagnosed by qPCR
Abstract
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is an uncommon manifestation of invasive pneumococcal disease and frequently occurs when an underlying hepatic disease is present. Bacterial identification through culture can be particularly challenging in patients with prior or concurrent antimicrobial use. DNA amplification detects very few copies of target DNA under ideal conditions in CSF or pleural effusion and, therefore, can be useful in selected infections. A culture-negative spontaneous pneumococcal peritonitis without preexisting peritoneal disease diagnosed by qPCR is herein described.
Keywords: Invasive pneumococcal disease; Real-time PCR; Spontaneous peritonitis; Streptococcus pneumoniae; lytA primer.
Figures
References
-
- Introduction of conventional and real time PCR for laboratory diagnostic of bacterial meningitis at Instituto Adolpho Lutz. Boletim Epidemiológico Paulista [Internet] 2007. Laboratório de Meningites Bacterianas, da Seção de Imunologia, do Instituto Adolfo Lutz – IAL, Coordenadoria de Controle de Doenças – CCD, Secretaria de Estado da Saúde de São Paulo – SES-SP.http://periodicos.ses.sp.bvs.br/pdf/bepa/v4n40/v4n40a03.pdf Apr; 4. Available from:
-
- Capdevila O., Pallares R., Grau I., Tubau F., Liñares J., Ariza J. Pneumococcal peritonitis in adult patients: report of 64 cases with special reference to emergence of antibiotic resistance. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(14):1742–1748. - PubMed
-
- Dumont R., Cinotti R., Lejus C., Caillon J., Boutoille D., Roquilly A. The microbiology of community-acquired peritonitis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30(2):131–135. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases