Expansive Suspension Laminoplasty Using a Spinous Process-Splitting Approach for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Surgical Technique and Outcomes Over 8 Years of Follow-up
- PMID: 30656246
- PMCID: PMC6324890
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-18-00008
Expansive Suspension Laminoplasty Using a Spinous Process-Splitting Approach for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Surgical Technique and Outcomes Over 8 Years of Follow-up
Abstract
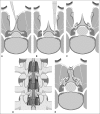
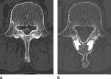
Introduction: To maximize the benefits of posterior decompression for severe multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis, we refined the expansive laminoplasty technique using a spinous process-splitting approach. This study tests the hypothesis that the surgical benefit of adequate decompression with posterior element preservation is maintained in the long term, over 8 years of follow-up.
Methods: Fifty-eight patients were followed up yearly for 8 years. Eight patients having nonlumbar spine surgery or Parkinson disease were excluded. The noninferiority of the 8-year versus peak-year outcomes was tested, with margins of 5 points for the Oswestry disability index and 1 point for the numeric rating scales (NRSs).
Results: In the 50 patients available for follow-up, the peak values of the mean improvements from baseline within the first 7 years were 35.8, 5.7, 5.9, and 2.8 points for the Oswestry disability index, low back pain NRS, leg pain NRS, and leg numbness NRS, respectively. The 95% lower confidence limits for the differences between the mean improvements from baseline at 8 years and the peak year were within the noninferiority margins for each scale.
Conclusion: Our technique was associated with substantial improvement from baseline for each scale. The initial improvements in function and symptoms were maintained for 8 years.
Figures

References
-
- Postacchini F, Cinotti G, Perugia D, Gumina S: The surgical treatment of central lumbar stenosis: Multiple laminotomy compared with total laminectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75:386-392. - PubMed
-
- Kakiuchi M, Fukushima W: Impact of spinous process integrity on ten to twelve-year outcomes after posterior decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: Study of open-door laminoplasty using a spinous process-splitting approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2015;97:1667-1677. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Kanamori M, Ishihara H, et al. : Clinical and radiographic results of expansive lumbar laminoplasty in patients with spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86:1698-1703. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, Matsumoto M, Ikegami T, et al. : Reduced postoperative wound pain after lumbar spinous process-splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis: A randomized controlled study. J Neurosurg Spine 2011;14:51-58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

