Austrian Experience with Lixisenatide Under Real-Life Conditions: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 30656523
- PMCID: PMC6437236
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-018-0558-2
Austrian Experience with Lixisenatide Under Real-Life Conditions: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Introduction: Lixisenatide has been studied extensively in randomized clinical trials; however, data on its use in the real-life practice are scarce.
Methods: This study was a prospective, 26-week, multicenter, observational study conducted in Austrian diabetes centers and office-based practices to evaluate efficacy and safety of lixisenatide under real-life conditions in patients with type 2 diabetes.
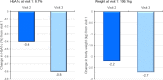
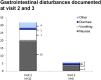
Results: Out of 144 patients (mean BMI 36.4 kg/m2, disease duration 12.4 years), 113 completed the documentation at 6 months and 42% received basal insulin with or without oral antidiabetic drugs. The HbA1c declined from 8.7% (72 mmol/mol) to 7.9% (63 mmol/mol) and at study end 24.8% of the patients reached an HbA1c level below 7%. Fasting and postprandial glucose after lixisenatide administration were reduced by 27 ± 58 mg/dl and 45 ± 67 mg/dl, respectively. At study end body weight (- 4.5 ± 5.4 kg), triglycerides (- 10.8 ± 105 mg/dl), systolic blood pressure (- 4.8 ± 17.1 mmHg), and LDL cholesterol (- 3.7 ± 25 mg/dl) were reduced. The most commonly reported adverse events were gastrointestinal disorders (18.8%). Forty-three patients (30%) discontinued prematurely, mostly caused by lack of efficacy, occurrence of gastrointestinal disorders, and missing reimbursement. The average dose of insulin decreased slightly by 1.5 units (from 29.4 to 27.9).
Conclusion: Lixisenatide demonstrated a similar efficacy and safety profile under real-life conditions as previously shown in randomized clinical trials.
Funding: sanofi-aventis GmbH Austria.
Keywords: HbA1c; Lixisenatide; PATIO; Real-life data; Short-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Lixisenatide as Add-On to Oral Antidiabetic Drugs as Part of Routine Clinical Practice in Bulgaria: LIXODAR Study.Diabetes Ther. 2019 Jun;10(3):981-993. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-0603-9. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Diabetes Ther. 2019. PMID: 30919317 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of lixisenatide for treatment of diabetes in the real world: data from the Monitoring Registry in a Real-Life Cohort in the Czech and Slovak Republic.Vnitr Lek. 2018 Spring;64(4):357-366. Vnitr Lek. 2018. PMID: 29791170 English.
-
Intensification of Basal Insulin Therapy with Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in a Real-World Setting: The BASAL-LIXI Study.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2018 Oct 9;89:37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2018.09.001. eCollection 2018. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2018. PMID: 30455779 Free PMC article.
-
Lixisenatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2013 Sep;49(9):537-53. doi: 10.1358/dot.2013.49.9.2020940. Drugs Today (Barc). 2013. PMID: 24086950 Review.
-
The design and discovery of lixisenatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014 Oct;9(10):1223-51. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.942638. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25119443 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct comparison two fixed-ratio combination glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist and basal insulin on glycemic and non glycemic parameters in type 2 diabetes.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Feb 1;23(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01282-w. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 36726134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centred approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015;58(3):429-42 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

