The Promises and Challenges of Erythropoietin for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30656553
- PMCID: PMC6407698
- DOI: 10.1007/s12017-019-08524-y
The Promises and Challenges of Erythropoietin for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
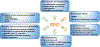
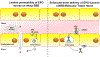
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder in the world, and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles and extracellular amyloid-beta protein deposits represent the major pathological hallmarks of the disease. Currently available treatments provide some symptomatic relief but fail to modify primary pathological processes that underlie the disease. Erythropoietin (EPO), a hematopoietic growth factor, acts primarily to stimulate erythroid cell production, and is clinically used to treat anemia. EPO has evolved as a therapeutic agent for neurodegeneration and has improved neurological outcomes and AD pathology in rodents. However, penetration of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and negative hematopoietic effects are the two major challenges for the therapeutic development of EPO for chronic neurodegenerative diseases like AD. The transferrin receptors at the BBB, which are responsible for transporting transferrin-bound iron from the blood into the brain parenchyma, can be used to shuttle therapeutic molecules across the BBB. In this review, we discuss the role of EPO as a potential neurotherapeutic for AD, challenges associated with EPO development for AD, and targeting the BBB transferrin receptor for EPO brain delivery.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Blood–brain barrier; Erythropoietin; Molecular Trojan horse; Transferrin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
None
Figures
References
-
- 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures (2018). Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 14(3), 367–429, doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.001. - DOI
-
- Armand-Ugon M, Aso E, Moreno J, Riera-Codina M, Sanchez A, Vegas E, et al. (2015). Memory Improvement in the AbetaPP/PS1 Mouse Model of Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Induced by Carbamylated-Erythropoietin is Accompanied by Modulation of Synaptic Genes. J Alzheimers Dis, 45(2), 407–421, doi: 10.3233/jad-150002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

