Impaired butyrate absorption in the proximal colon, low serum butyrate and diminished central effects of butyrate on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 30656835
- PMCID: PMC7199780
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.13256
Impaired butyrate absorption in the proximal colon, low serum butyrate and diminished central effects of butyrate on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
Aim: Butyrate is a major gut microbiota-derived metabolite. Reduced butyrate-producing bacteria has been reported in the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR), a model of hypertension characterized by dysfunctional autonomic nervous system and gut dysbiosis. Here, we demonstrate a potential mechanism for butyrate in blood pressure regulation.
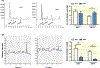
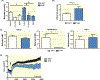
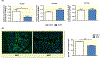
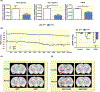
Methods: High-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry were performed to measure butyrate levels in feces and serum. Ussing chamber determined butyrate transport in colon ex vivo. Real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry evaluated expression of butyrate transporter, Slc5a8, in the colon. Mean arterial blood pressure was measured in catheterized anesthetized rats before and after a single butyrate intracerebroventricular injection. Activity of cardioregulatory brain regions was determined by functional magnetic resonance imaging to derive neural effects of butyrate.
Results: In the SHR, we demonstrated elevated butyrate levels in cecal content, but diminished butyrate levels in circulation, possibly due to reduced expression of Slc5a8 transporter in the colon. In addition, we observed lower expression levels of butyrate-sensing receptors in the hypothalamus of SHR, likely leading to the reduced effects of centrally administered butyrate on blood pressure in the SHR. Functional magnetic resonance imaging revealed reduced activation of cardioregulatory brain regions following central administration of butyrate in the SHR compared to control.
Conclusion: We demonstrated a reduced availability of serum butyrate in the SHR, possibly due to diminished colonic absorption. Reduced expression of butyrate-sensing receptors in the SHR hypothalamus may explain the reduced central responsiveness to butyrate, indicating microbial butyrate may play a role in blood pressure regulation.
Keywords: absorption; blood pressure; butyrate; gut microbiota; neuronal activity.
© 2019 Scandinavian Physiological Society. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Bordin M, D’Atri F, Guillemot L, Citi S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate the expression of tight junction proteins. Mol Cancer Res. 2004;2(12):692–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

