The impact of different rheumatic diseases on health-related quality of life: a comparison with a selected sample of healthy individuals using SF-36 questionnaire, EQ-5D and SF-6D utility values
- PMID: 30657123
- PMCID: PMC6502108
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v89i4.7298
The impact of different rheumatic diseases on health-related quality of life: a comparison with a selected sample of healthy individuals using SF-36 questionnaire, EQ-5D and SF-6D utility values
Abstract
Background: Given the high prevalence of rheumatic diseases, there is a need to determine which conditions have the greatest impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The main aim of this study was to explore the HRQoL scores among 14 different rheumatic diseases and to compare them with the results of a selecting sample of healthy controls.
Methods: 2633 patients of an ongoing cohort have been enrolled. Rheumatic diseases were classified into five diagnostic groups: inflammatory rheumatic diseases, connective tissue disorders, symptomatic peripheral osteoarthritis, soft tissue disorders, and osteoporosis. For comparison were used 649 healthy controls. The HRQoL was evaluated with the Medical Outcomes Study Short-Form 36 Health Survey (SF-36), the EuroQol five Dimensions (EQ-5D) questionnaire, and the Short-Form six Dimensions (SF-6D) questionnaire.
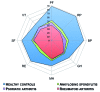
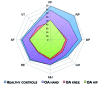
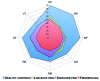
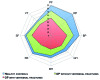
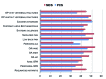
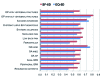
Results: The five major rheumatic disease groups, compared to healthy people, significantly impaired all eight health concepts of the SF-36 (p <0.0001). Similar results were found for EQ-5D and SF-6D. The patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases have poorer self-reported health status than those without arthritis in all domains of living, but particularly with respect to scales measuring aspects of physical functioning or mobility, role limitation due to physical health problems and usual activities, and bodily pain. Rheumatoid arthritis had the largest negative impact on HRQoL, followed by fibromyalgia, vertebral fractures due to osteoporosis, hip osteoarthritis, and systemic sclerosis.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that rheumatic diseases have a clearly detrimental effect on the HRQoL, and physical domain is more impaired than mental and social ones.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health-related quality of life among adults with arthritis-Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 11 states, 1996-1998. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 2000;49(17):366–9. - PubMed
-
- March L, Smith EU, Hoy DG, Cross MJ, Sanchez-Riera L, Blyth F, et al. Burden of disability due to musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(3):353–66. - PubMed
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Carmona L, Wolfe F, Vos T, et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1316–22. - PubMed
-
- Hoy DG, Smith E, Cross M, Sanchez-Riera L, Buchbinder R, Blyth FM, et al. The global burden of musculoskeletal conditions for 2010: an overview of methods. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):982–9. - PubMed
-
- WHO Scientific Group on the Burden of Musculoskeletal Conditions at the Start of the New Millennium. The burden of musculoskeletal conditions at the start of the new millennium. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2003;919:1–218. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

