Spatial and temporal changes in myogenic protein expression by the microenvironment after freeze injury
- PMID: 30657171
- PMCID: PMC6365476
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12925
Spatial and temporal changes in myogenic protein expression by the microenvironment after freeze injury
Abstract
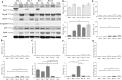
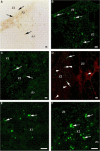
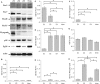
Skeletal muscle has the remarkable capability to regenerate itself following injury. Adult myogenic stem cells (MSCs) are responsible for the repair and regeneration, and their activity is controlled by intrinsic and extrinsic factors. The aim of this study was to examine and compare the expression levels of Pax3, Pax7, MRF and p38 proteins during the course of regeneration and in different areas of the focal freeze-lesion damaged adult rat TA muscle. Using the focal freeze injury model, immunohistochemistry, laser-capture micro-dissection and Western blot analysis were performed. The results show that (1) in the severely damaged area, the focal freeze-lesion injury significantly activated Pax7 and myogenin expression within 7 days and down-regulated Pax3, MyoD and Myf-5 within 1 or 3 days, and (2) the level of the p38 protein was strongly and transiently up-regulated in the whole muscle on day 7 following injury, whereas the level of the pp38 protein was down-regulated within 3 days in the severely damaged and non-damaged areas. These findings indicate that the temporal (e.g. the time course of regeneration) and spatial (e.g. three zones created by the focal freeze-lesion) cues in a regenerating muscle have a significant impact on the activity of the adult MSCs.
Keywords: Pax; microenvironment; muscle regeneration; myogenic regulatory factor; myogenic stem cells.
© 2019 Anatomical Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and neural control of myogenic regulatory factor genes during regeneration of mouse soleus.J Histochem Cytochem. 2001 Jul;49(7):887-99. doi: 10.1177/002215540104900709. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001. PMID: 11410613
-
Embryonic myogenesis pathways in muscle regeneration.Dev Dyn. 2004 Feb;229(2):380-92. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10457. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 14745964
-
Expression of myogenic regulatory factors and myo-endothelial remodeling in sporadic inclusion body myositis.Neuromuscul Disord. 2013 Jan;23(1):75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Neuromuscul Disord. 2013. PMID: 23058947 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of satellite cell activation during muscle regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011 Apr 19;2(2):18. doi: 10.1186/scrt59. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21542881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAX3 and PAX7 as upstream regulators of myogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Aug;44:115-25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.09.017. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26424495 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mitochondria in Mediation of Skeletal Muscle Repair.Muscles. 2023 Mar 24;2(2):119-163. doi: 10.3390/muscles2020011. Muscles. 2023. PMID: 40757564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong DM, Brady R, Hersh LB, et al. (1991) Expression of choline acetyltransferase and nerve growth factor receptor within hypoglossal motoneurons following nerve injury. J Comp Neurol 304, 596–607. - PubMed
-
- Bodine‐Fowler S (1994) Skeletal muscle regeneration after injury: an overview. J Voice 8, 53–62. - PubMed
-
- Cabane C, Englaro W, Yeow K, et al. (2003) Regulation of C2C12 myogenic terminal differentiation by MKK3/p38alpha pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284, C658–C666. - PubMed
-
- Charge SB, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84, 209–238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

