Spinning convincing stories for both true and false association signals
- PMID: 30657194
- PMCID: PMC6590226
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.22189
Spinning convincing stories for both true and false association signals
Abstract
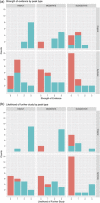
When interpreting genome-wide association peaks, it is common to annotate each peak by searching for genes with plausible relationships to the trait. However, "all that glitters is not gold"-one might interpret apparent patterns in the data as plausible even when the peak is a false positive. Accordingly, we sought to see how human annotators interpreted association results containing a mixture of peaks from both the original trait and a genetically uncorrelated "synthetic" trait. Two of us prepared a mix of original and synthetic peaks of three significance categories from five different scans along with relevant literature search results and then we all annotated these regions. Three annotators also scored the strength of evidence connecting each peak to the scanned trait and the likelihood of further studying that region. While annotators found original peaks to have stronger evidence (p Bonferroni = 0.017) and higher likelihood of further study ( p Bonferroni = 0.006) than synthetic peaks, annotators often made convincing connections between the synthetic peaks and the original trait, finding these connections 55% of the time. These results show that it is not difficult for annotators to make convincing connections between synthetic association signals and genes found in those regions.
Keywords: association peaks; false positives; genome-wide association studies; literature review.
© 2019 The Authors. Genetic Epidemiology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Dowle, M. A. S. (2017). data.table: Extension of ‘data.frame’ (version 1.10.4). CRAN. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=data.table
-
- Kovalchik, S. (2017). RISmed: Download content from NCBI databases (Version 2.1.7) [Package]. CRAN: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RISmed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

