A multi-level response to DNA damage induced by aluminium
- PMID: 30657222
- PMCID: PMC6850279
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.14231
A multi-level response to DNA damage induced by aluminium
Abstract
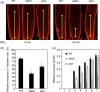
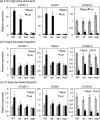
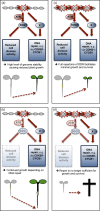
Aluminium (Al) ions are one of the primary growth-limiting factors for plants on acid soils, globally restricting agriculture. Despite its impact, little is known about Al action in planta. Earlier work has indicated that, among other effects, Al induces DNA damage. However, the loss of major DNA damage response regulators, such SOG1, partially suppressed the growth reduction in plants seen on Al-containing media. This raised the question whether Al actually causes DNA damage and, if so, how. Here, we provide cytological and genetic data corroborating that exposure to Al leads to DNA double-strand breaks. We find that the Al-induced damage specifically involves homology-dependent (HR) recombination repair. Using an Al toxicity assay that delivers higher Al concentrations than used in previous tests, we find that sog1 mutants become highly sensitive to Al. This indicates a multi-level response to Al-induced DNA damage in plants.
Keywords: ATM; ATR; Arabidopsis thaliana; CDKB1; DNA damage; RAD51; SOG1; aluminium; growth; homologous recombination repair.
© 2019 The Authors. The Plant Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that none of them has a conflict of interest with the here‐presented data.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Aluminum-Dependent Terminal Differentiation of the Arabidopsis Root Tip Is Mediated through an ATR-, ALT2-, and SOG1-Regulated Transcriptional Response.Plant Cell. 2015 Sep;27(9):2501-15. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00172. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Plant Cell. 2015. PMID: 26320227 Free PMC article.
-
The multi-BRCT domain protein DDRM2 promotes the recruitment of RAD51 to DNA damage sites to facilitate homologous recombination.New Phytol. 2023 May;238(3):1073-1084. doi: 10.1111/nph.18787. Epub 2023 Mar 4. New Phytol. 2023. PMID: 36727295
-
SOG1 and BRCA1 Interdependently Regulate RAD54 Expression for Repairing Salinity-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2024 May 30;65(5):708-728. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcae008. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38242160
-
An insight into the mechanism of DNA damage response in plants- role of SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1: An overview.Mutat Res. 2020 Jan-Apr;819-820:111689. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111689. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32004947 Review.
-
SOG1: a master regulator of the DNA damage response in plants.Genes Genet Syst. 2016;90(4):209-16. doi: 10.1266/ggs.15-00011. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Genes Genet Syst. 2016. PMID: 26617076 Review.
Cited by
-
SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1 plays rice-specific roles in DNA damage response and repair.Plant Physiol. 2023 Feb 12;191(2):1288-1304. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac490. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36271862 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Pyrone-Fused Tricyclic Scaffold-based Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Al3+ Detection.J Fluoresc. 2025 Jun;35(6):4559-4568. doi: 10.1007/s10895-024-03864-w. Epub 2024 Jul 23. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 39042359
-
Systematic Investigation of Aluminum Stress-Related Genes and Their Critical Roles in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9045. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169045. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and regulation of aluminum-induced secretion of organic acid anions from plant roots.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019 Jun;20(6):513-527. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900188. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019. PMID: 31090277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Instability Is an Early Event in Aluminium-Induced Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 7;21(23):9332. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239332. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33297592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bleuyard, J.Y. , Gallego, M.E. , Savigny, F. and White, C.I. (2005) Differing requirements for the Arabidopsis Rad51 paralogs in meiosis and DNA repair. Plant J. 41, 533–545. - PubMed
-
- Bray, C.M. and West, C.E. (2005) DNA repair mechanisms in plants: crucial sensors and effectors for the maintenance of genome integrity. New Phytol. 168, 511–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

