Association between the LIPG polymorphisms and serum lipid levels in the Maonan and Han populations
- PMID: 30657227
- PMCID: PMC6590183
- DOI: 10.1002/jgm.3071
Association between the LIPG polymorphisms and serum lipid levels in the Maonan and Han populations
Abstract
Introduction: The Maonan population is a relatively isolated minority in China. Little is known about endothelial lipase gene (LIPG) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and serum lipid levels in the Chinese populations. The present study aimed to detect the association of several LIPG SNPs and environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Chinese Maonan and Han populations.
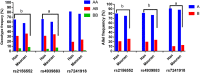
Methods: In total, 773 subjects of Maonan ethnicity and 710 participants of Han ethnicity were randomly selected from our previous stratified randomized samples. Genotypes of the LIPG rs2156552, rs4939883 and rs7241918 SNPs were determined by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism, and then confirmed by direct sequencing.
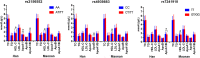
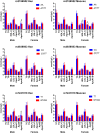
Results: The allelic (rs2156552, rs4939883 and rs7241918) and genotypic (rs2156552 and rs4939883) frequencies were different between the two ethnic groups (p < 0.05-0.01). The minor allele carriers had lower apolipoprotein (Apo)A1/ApoB ratio (rs2156552 and rs7241918), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and apolipoprotein (Apo)A1 (rs2156552) levels and higher ApoB levels (rs4939883) in the Han population, and lower HDL-C (rs2156552, rs4939883 and rs7241918) levels in the Maonan minority than the minor allele non-carriers (p < 0.0167 after Bonferroni correction). Subgroup analyses according to sex showed that the minor allele carriers had a lower ApoA1/ApoB ratio (rs2156552 and rs7241918) and higher ApoB levels (rs7241918) in Han males, and lower ApoA1 and HDL-C levels in Maonan females than the minor allele non-carriers (p < 0.0167-0.001).
Conclusions: The present study demonstrates the association between the LIPG polymorphsims and serum lipid levels in the two ethnic groups. These associations might have an ethnic- and or/sex-specificity.
Keywords: endothelial lipase; environmental factors; lipids; single nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2019 The Authors. The Journal of Gene Medicine Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association of the LIPG 584C > T polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Bai Ku Yao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Oct 6;9:110. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-110. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20923576 Free PMC article.
-
LIPG SNPs, their haplotypes and gene-environment interactions on serum lipid levels.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jan 8;18(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0942-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30621702 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of the APOA1 rs964184 SNP and serum lipid traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 May 10;17(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0759-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29747660 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the MLXIPL/TBL2 rs17145738 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2013 Oct 25;12:156. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-156. Lipids Health Dis. 2013. PMID: 24160749 Free PMC article.
-
CHIMGEN: a Chinese imaging genetics cohort to enhance cross-ethnic and cross-geographic brain research.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Mar;25(3):517-529. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0627-6. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31827248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of PRKN-PACRG SNPs and G × G and G × E interactions with the risk of hyperlipidaemia.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 3;10(1):13010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68826-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32747620 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between the APOB rs1042034 SNP and Blood Lipid Characteristics of 2 Ethnic Groups in China.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019 Jan-Dec;25:1076029619892088. doi: 10.1177/1076029619892088. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019. PMID: 31833377 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between TUBB-WWOX SNPs, their haplotypes, gene-gene, and gene-environment interactions and dyslipidemia.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Feb 17;13(4):5906-5927. doi: 10.18632/aging.202514. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33612478 Free PMC article.
-
SYNE1-QK1 SNPs, G × G and G × E interactions on the risk of hyperlipidaemia.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(10):5772-5785. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15239. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32281752 Free PMC article.
-
EHBP1 SNPs, Their Haplotypes, and Gene-Environment Interactive Effects on Serum Lipid Levels.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 27;5(13):7158-7169. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03522. eCollection 2020 Apr 7. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32280856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis GF, Rader DJ. New insights into the regulation of HDL metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Circ Res. 2005;96:1221‐1232. - PubMed
-
- Gotto AM Jr, Brinton EA. Assessing low levels of high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol as a risk factor in coronary heart disease. A Working Group Report and Update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:717‐724. - PubMed
-
- Hooper L, Summerbell CD, Thompson R, et al. Reduced or modified dietary fat for preventing cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2013;28:204‐205. - PubMed
-
- Watts GF, Ooi EMM, Chan DC. Demystifying the management of hypertriglyceridaemia. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013;10:648‐661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

