The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor mediates plasminogen-induced efferocytosis
- PMID: 30657605
- PMCID: PMC6392118
- DOI: 10.1002/JLB.1AB0417-160RR
The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor mediates plasminogen-induced efferocytosis
Abstract
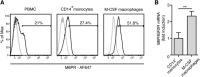
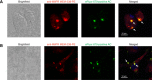
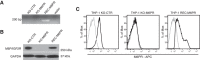
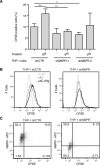
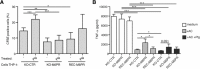
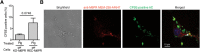
The plasminogen system is harnessed in a wide variety of physiological processes, such as fibrinolysis, cell migration, or efferocytosis; and accordingly, it is essential upon inflammation, tissue remodeling, wound healing, and for homeostatic maintenance in general. Previously, we identified a plasminogen receptor in the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R, CD222). Here, we demonstrate by means of genetic knockdown, knockout, and rescue approaches combined with functional studies that M6P/IGF2R is up-regulated on the surface of macrophages, recognizes plasminogen exposed on the surface of apoptotic cells, and mediates plasminogen-induced efferocytosis. The level of uptake of plasminogen-coated apoptotic cells inversely correlates with the TNF-α production by phagocytes indicating tissue clearance without inflammation by this mechanism. Our results reveal an up-to-now undetermined function of M6P/IGF2R in clearance of apoptotic cells, which is crucial for tissue homeostasis.
Keywords: M6P/IGF2R; efferocytosis; macrophages; plasminogen; tissue homeostasis.
©2019 The Authors. Society for Leukocyte Biology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dissecting mannose 6-phosphate-insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor complexes that control activation and uptake of plasminogen in cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22450-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.339663. Epub 2012 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22613725 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble M6P/IGF2R released by TACE controls angiogenesis via blocking plasminogen activation.Circ Res. 2011 Mar 18;108(6):676-85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234732. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21273553
-
Mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor mediates the growth-inhibitory effects of retinoids.Cell Growth Differ. 1999 Aug;10(8):591-600. Cell Growth Differ. 1999. PMID: 10470859
-
The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R), a putative breast tumor suppressor gene.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998 Feb;47(3):269-81. doi: 10.1023/a:1005959218524. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998. PMID: 9516081 Review.
-
Mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R) in carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2010 Mar 1;289(1):11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.06.036. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Cancer Lett. 2010. PMID: 19646808 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor is a key immune-related gene that is correlated with a poor prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: A bioinformatics analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 18;12:871786. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.871786. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36330486 Free PMC article.
-
The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid CD44 as a marker for pulmonary fibrosis in diffuse parenchymal lung diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 13;15:1479458. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1479458. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39872532 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of cell-specific peripheral blood biomarkers in severe allergic asthma identifies innate immune dysfunction.Clin Exp Allergy. 2022 Nov;52(11):1334-1337. doi: 10.1111/cea.14197. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Clin Exp Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35892202 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Blockade of TMPRSS2-mediated priming of SARS-CoV-2 by lactoferricin.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 23;13:958581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.958581. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36081512 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Receptor Isoforms and Insulin Growth Factor-like Receptors: Implications in Cell Signaling, Carcinogenesis, and Chemoresistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 9;24(19):15006. doi: 10.3390/ijms241915006. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dano K, Behrendt N, Hoyer‐Hansen G, et al. Plasminogen activation and cancer. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:676–681. - PubMed
-
- Dotti CG, Galvan C, Ledesma MD. Plasmin deficiency in Alzheimer's disease brains: causal or casual?. Neurodegener Dis. 2004;1:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Gyetko MR, Aizenberg D, Mayo‐Bond L. Urokinase‐deficient and urokinase receptor‐deficient mice have impaired neutrophil antimicrobial activation in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:648–656. - PubMed
-
- O'Mullane MJ, Baker MS. Loss of cell viability dramatically elevates cell surface plasminogen binding and activation. Exp Cell Res. 1998;242:153–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

