Developmental cost of leg-regenerated Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)
- PMID: 30657777
- PMCID: PMC6338371
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210615
Developmental cost of leg-regenerated Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)
Abstract
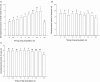
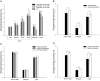
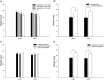
As larval cannibalism is common under intensive rearing conditions, leg regeneration can help ladybugs adapt to the competitive environment, but whether the leg regeneration leads to side effects on development remains unclear. To analyze the potentially developmental cost of leg regeneration, the developmental period and weight of leg-regenerated Coccinella septempunctata were studied in the laboratory. The results showed that, when the time intervals between the emergency of 4th-instar larva and leg amputation increased, the developmental period of leg-regenerated 4th-instar larvae was gradually prolonged. Significantly developmental delay were also examined at prepupal and pupal stages, and various timings of leg amputation affected the periods of leg-regenerated prepupae/pupae similarly. After the leg was amputated at different larval instars, the developmental delay only occurred at the larval instar when the leg was amputated, whereas other larval instars failed to be extended, and the developmental periods of leg-regenerated prepupae/pupae were affected similarly by the instars of leg amputation. Developmental delays possibly resulted in more consumption by leg-regenerated larvae, and then weight gains at prepupal/pupal stages, but different larval instars of leg amputation affected the weight gain similarly. Both the developmental delay (at 4th-instar larval, prepupal and pupal stages) and weight gain (at pupal and adult stages) in complete/bilateral amputation were longer or greater than those in half/unilateral amputation. However, the thoracic locations of leg amputation impacted the developmental delay and weight gain similarly. Our study indicates that although leg regeneration triggers the developmental cost decreasing the competitive superiority or agility, C. septempunctata larvae still choose to completely regenerate the leg to adapt to complex environments. Thus, in order to remain competitive at adult stages, leg-impaired larvae may make an investment tradeoff between leg regeneration and developmental cost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential investment tradeoff between offspring production and functional recovery promoted by larval cannibalism in Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: coccinellidae).Pest Manag Sci. 2019 Feb;75(2):484-491. doi: 10.1002/ps.5145. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Pest Manag Sci. 2019. PMID: 30022594
-
Isoform specific roles of Broad-Complex in larval development in Leptinotarsa decemlineata.Insect Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;28(3):420-430. doi: 10.1111/imb.12563. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Insect Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30632239
-
[Adult leg development of Tenebrio molitor: I. Experimental analysis of the restoration process during morphogenesis (author's transl)].J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Apr;35(2):303-21. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976. PMID: 939941 French.
-
Interactions of the Asian Lady Beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), and the North American Native Lady Beetle, Coccinella novemnotata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Prospects for Recovery Post-Decline.Environ Entomol. 2017 Feb 1;46(1):21-29. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvw153. Environ Entomol. 2017. PMID: 28049630
-
Development times and age-specific life table parameters of the native lady beetle species Coccinella novemnotata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and its invasive congener Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae).Environ Entomol. 2014 Aug;43(4):1067-75. doi: 10.1603/EN14053. Environ Entomol. 2014. PMID: 25182621
References
-
- Gui JF, Yi MS (2002) Developmental Biology, Science Press, Beijing, China. 154 pp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

