LFMM 2: Fast and Accurate Inference of Gene-Environment Associations in Genome-Wide Studies
- PMID: 30657943
- PMCID: PMC6659841
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msz008
LFMM 2: Fast and Accurate Inference of Gene-Environment Associations in Genome-Wide Studies
Abstract
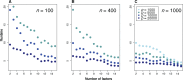
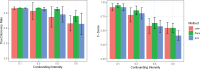
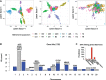
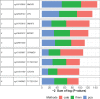
Gene-environment association (GEA) studies are essential to understand the past and ongoing adaptations of organisms to their environment, but those studies are complicated by confounding due to unobserved demographic factors. Although the confounding problem has recently received considerable attention, the proposed approaches do not scale with the high-dimensionality of genomic data. Here, we present a new estimation method for latent factor mixed models (LFMMs) implemented in an upgraded version of the corresponding computer program. We developed a least-squares estimation approach for confounder estimation that provides a unique framework for several categories of genomic data, not restricted to genotypes. The speed of the new algorithm is several order faster than existing GEA approaches and then our previous version of the LFMM program. In addition, the new method outperforms other fast approaches based on principal component or surrogate variable analysis. We illustrate the program use with analyses of the 1000 Genomes Project data set, leading to new findings on adaptation of humans to their environment, and with analyses of DNA methylation profiles providing insights on how tobacco consumption could affect DNA methylation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Software availability: Software is available in the R package lfmm at https://bcm-uga.github.io/lfmm/.
Keywords: confounding factors; ecological genomics; gene-environment association; local adaptation; statistical methods.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LEA 3: Factor models in population genetics and ecological genomics with R.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021 Nov;21(8):2738-2748. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13366. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021. PMID: 33638893
-
Testing for associations between loci and environmental gradients using latent factor mixed models.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Jul;30(7):1687-99. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst063. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23543094 Free PMC article.
-
Expanded utility of the R package, qgg, with applications within genomic medicine.Bioinformatics. 2023 Nov 1;39(11):btad656. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad656. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37882742 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Studies of Local Adaptation in Natural Plant Populations.J Hered. 2017 Dec 21;109(1):3-15. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esx091. J Hered. 2017. PMID: 29045754 Review.
-
Software engineering the mixed model for genome-wide association studies on large samples.Brief Bioinform. 2009 Nov;10(6):664-75. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbp050. Brief Bioinform. 2009. PMID: 19933212 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for Admixture and Rapid Evolution During Glacial Climate Change in an Alpine Specialist.Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Jul 3;41(7):msae130. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae130. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38935588 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent selection and climate adaptation fuel genomic differentiation between sister species of Sphagnum (peat moss).Ann Bot. 2023 Nov 23;132(3):499-512. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad104. Ann Bot. 2023. PMID: 37478307 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Neutral Recombination Variation on Genome Scans for Selection.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Jun 5;9(6):1851-1867. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400088. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30971391 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Scale Data Reveal Deep Lineage Divergence and a Complex Demographic History in the Texas Horned Lizard (Phrynosoma cornutum) throughout the Southwestern and Central United States.Genome Biol Evol. 2022 Jan 4;14(1):evab260. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evab260. Genome Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 34849831 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape genomics reveals adaptive genetic differentiation driven by multiple environmental variables in naked barley on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.Heredity (Edinb). 2023 Dec;131(5-6):316-326. doi: 10.1038/s41437-023-00647-0. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Heredity (Edinb). 2023. PMID: 37935814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Mita S, Thuillet AC, Gay L, Ahmadi N, Manel S, Ronfort J, Vigouroux Y.. 2013. Detecting selection along environmental gradients: analysis of eight methods and their effectiveness for outbreeding and selfing populations. Mol Ecol. 22(5):1383–1399. - PubMed
-
- Devlin B, Roeder K.. 1999. Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 55(4):997–1004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

