Mass Spectrometry Analysis and Biological Characterization of the Predatory Ant Odontomachus monticola Venom and Venom Sac Components
- PMID: 30658410
- PMCID: PMC6356579
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins11010050
Mass Spectrometry Analysis and Biological Characterization of the Predatory Ant Odontomachus monticola Venom and Venom Sac Components
Abstract
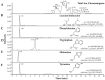
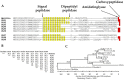
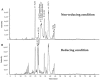
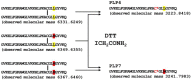
We previously identified 92 toxin-like peptides and proteins, including pilosulin-like peptides 1⁻6 from the predatory ant Odontomachus monticola, by transcriptome analysis. Here, to further characterize venom components, we analyzed the venom and venom sac extract by ESI-MS/MS with or without trypsin digestion and reducing agent. As the low-molecular-mass components, we found amino acids (leucine/isoleucine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan) and biogenic amines (histamine and tyramine) in the venom and venom sac extract. As the higher molecular mass components, we found peptides and proteins such as pilosulin-like peptides, phospholipase A₂s, hyaluronidase, venom dipeptidyl peptidases, conotoxin-like peptide, and icarapin-like peptide. In addition to pilosulin-like peptides 1⁻6, we found three novel pilosulin-like peptides that were overlooked by transcriptome analysis. Moreover, pilosulin-like peptides 1⁻6 were chemically synthesized, and some of them displayed antimicrobial, hemolytic, and histamine-releasing activities.
Keywords: ant; mass spectrometry analysis; pilosulin-like peptide; venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined Venom Gland Transcriptomic and Venom Peptidomic Analysis of the Predatory Ant Odontomachus monticola.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Oct 13;9(10):323. doi: 10.3390/toxins9100323. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29027956 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of peptides and low molecular weight components of the giant ant Dinoponera quadriceps venom.Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 28;401(8):945-954. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2019-0397. Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32229648
-
Characterisation of major peptides in 'jack jumper' ant venom by mass spectrometry.Toxicon. 2004 Feb;43(2):173-83. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.021. Toxicon. 2004. PMID: 15019477
-
Pilosulins: a review of the structure and mode of action of venom peptides from an Australian ant Myrmecia pilosula.Toxicon. 2015 May;98:54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Toxicon. 2015. PMID: 25725257 Review.
-
The Biochemical Toxin Arsenal from Ant Venoms.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jan 20;8(1):30. doi: 10.3390/toxins8010030. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26805882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Peptide Venom Composition of the Fierce Stinging Ant Tetraponera aethiops (Formicidae: Pseudomyrmecinae).Toxins (Basel). 2019 Dec 14;11(12):732. doi: 10.3390/toxins11120732. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31847368 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptide Arsenal Predicted from the Venom Gland Transcriptome of the Tropical Trap-Jaw Ant Odontomachus chelifer.Toxins (Basel). 2023 May 18;15(5):345. doi: 10.3390/toxins15050345. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37235379 Free PMC article.
-
Bottom-Up Proteomic Analysis of Polypeptide Venom Components of the Giant Ant Dinoponera Quadriceps.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jul 29;11(8):448. doi: 10.3390/toxins11080448. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31362422 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an Insect Neuroactive Helix Ring Peptide from Ant Venom.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Oct 5;15(10):600. doi: 10.3390/toxins15100600. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37888631 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic approach to characterize the venom of the parasitic wasp Cotesia congregata (Hymenoptera: Braconidae).BMC Genomics. 2025 Apr 30;26(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11604-y. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40307720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torres A.F., Huang C., Chong C.M., Leung S.W., Prieto-da-Silva A.R., Havt A., Quinet Y.P., Martins A.M., Lee S.M., Radis-Baptista G. Transcriptome analysis in venom gland of the predatory giant ant Dinoponera quadriceps: Insights into the polypeptide toxin arsenal of hymenopterans. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e87556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robinson S.D., Mueller A., Clayton D., Starobova H., Hamilton B.R., Payne R.J., Vetter I., King G.F., Undheim E.A.B. A comprehensive portrait of the venom of the giant red bull ant, Myrmecia gulosa, reveals a hyperdiverse hymenopteran toxin gene family. Sci. Adv. 2018;4:eaau4640. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau4640. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

