Anti-Depressive Effectiveness of Baicalin In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 30658416
- PMCID: PMC6359445
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24020326
Anti-Depressive Effectiveness of Baicalin In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
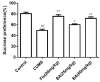
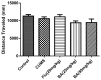
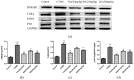
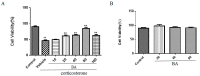
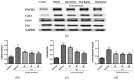
Baicalin (BA), a major polyphenol compound isolated from the extracts of Scutellaria radix, has been previously reported to ameliorate depressive-like behaviors in mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). However, its underlying antidepressant mechanisms remain unclear. This study was designed to confirm the antidepressant-like effects of BA on CUMS induced behavioral abnormalities in mice, and sought to explore the pharmacological mechanisms in vivo and in vitro. The CUMS procedure was carried out to induce depression in mice. Afterwards, the tail suspension test (TST), forced swim test (FST), and open field test (OFT) were performed within 24 h, then sucrose preference test (SPT) was conducted. Additionally, PC12 cells were pretreated with BA for 2 h, then further stimulated with corticosterone for 24 h. The levels of Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) in serum, hippocampus homogenate and cell culture medium were determined using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The protein expressions of inhibition of high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1)/Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathways in hippocampus and PC12 cells were detected. Our results showed that CUMS-treated mice presented notable depressive-like symptoms, such as decreased sucrose consumption, increased FST and TST immobility time. While BA (25, 50 mg/kg) significantly attenuated these changes. Besides, BA treatment considerably inhibited inflammatory cytokinesl (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) levels in serum, hippocampus homogenate and cell culture medium. Western blot analysis indicated that BA inhibited the expressions of HMGB1, TLR4, and p-NF-κBp65 both in vivo and in vitro. In conclusion, the present study confirmed that BA possessed efficient antidepressant effects on depression, which was possibly related to the inhibition of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathways.
Keywords: HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB; antidepressant; baicalin; chronic unpredictable mild stress; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
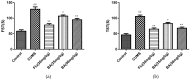
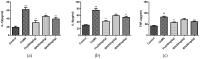
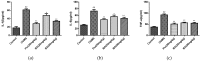
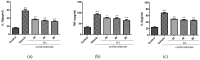
References
-
- Kiosses D.N., Gross J.J., Banerjee S., Duberstein P.R., Putrino D., Alexopoulos G.S. Negative emotions and suicidal ideation during psychosocial treatments in older adults with major depression and cognitive impairment. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 2017;25:620–629. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2017.01.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

