Identification of Prognostic Biomarker Signatures and Candidate Drugs in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from Systems Biology Analysis
- PMID: 30658502
- PMCID: PMC6359148
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina55010020
Identification of Prognostic Biomarker Signatures and Candidate Drugs in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from Systems Biology Analysis
Abstract
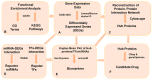
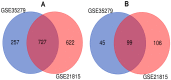
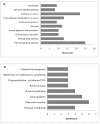
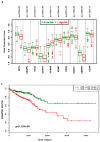
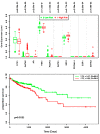
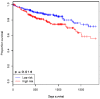
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most common cause of cancer-related death in the world, but early diagnosis ameliorates the survival of CRC. This report aimed to identify molecular biomarker signatures in CRC. We analyzed two microarray datasets (GSE35279 and GSE21815) from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) to identify mutual differentially expressed genes (DEGs). We integrated DEGs with protein⁻protein interaction and transcriptional/post-transcriptional regulatory networks to identify reporter signaling and regulatory molecules; utilized functional overrepresentation and pathway enrichment analyses to elucidate their roles in biological processes and molecular pathways; performed survival analyses to evaluate their prognostic performance; and applied drug repositioning analyses through Connectivity Map (CMap) and geneXpharma tools to hypothesize possible drug candidates targeting reporter molecules. A total of 727 upregulated and 99 downregulated DEGs were detected. The PI3K/Akt signaling, Wnt signaling, extracellular matrix (ECM) interaction, and cell cycle were identified as significantly enriched pathways. Ten hub proteins (ADNP, CCND1, CD44, CDK4, CEBPB, CENPA, CENPH, CENPN, MYC, and RFC2), 10 transcription factors (ETS1, ESR1, GATA1, GATA2, GATA3, AR, YBX1, FOXP3, E2F4, and PRDM14) and two microRNAs (miRNAs) (miR-193b-3p and miR-615-3p) were detected as reporter molecules. The survival analyses through Kaplan⁻Meier curves indicated remarkable performance of reporter molecules in the estimation of survival probability in CRC patients. In addition, several drug candidates including anti-neoplastic and immunomodulating agents were repositioned. This study presents biomarker signatures at protein and RNA levels with prognostic capability in CRC. We think that the molecular signatures and candidate drugs presented in this study might be useful in future studies indenting the development of accurate diagnostic and/or prognostic biomarker screens and efficient therapeutic strategies in CRC.
Keywords: biomarkers; candidate drugs; colorectal cancer; differentially expressed genes; drug repositioning; protein–protein interaction; reporter biomolecules; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of candidate biomarkers and therapeutic drugs of colorectal cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Med Oncol. 2020 Oct 19;37(11):104. doi: 10.1007/s12032-020-01425-2. Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33078282
-
Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated bioinformatics analysis.Gene. 2019 Apr 15;692:119-125. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30654001
-
Identifying the key genes and microRNAs in colorectal cancer liver metastasis by bioinformatics analysis and in vitro experiments.Oncol Rep. 2019 Jan;41(1):279-291. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6840. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30542696 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Potential candidates for diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb;233(2):901-913. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25801. Epub 2017 May 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28092102 Review.
-
Integration of genetic variants and gene network for drug repurposing in colorectal cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Nov;161:105203. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105203. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32950641
Cited by
-
Network-Based Data Analysis Reveals Ion Channel-Related Gene Features in COVID-19: A Bioinformatic Approach.Biochem Genet. 2023 Apr;61(2):471-505. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10280-x. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 36104591 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional dysregulation of TRIM29 promotes colorectal cancer carcinogenesis via pyruvate kinase-mediated glucose metabolism.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jan 20;13(4):5034-5054. doi: 10.18632/aging.202414. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33495406 Free PMC article.
-
Centromere protein N may be a novel malignant prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.PeerJ. 2021 May 3;9:e11342. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11342. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33987018 Free PMC article.
-
miR-615 Fine-Tunes Growth and Development and Has a Role in Cancer and in Neural Repair.Cells. 2020 Jun 27;9(7):1566. doi: 10.3390/cells9071566. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32605009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics Prediction and Machine Learning on Gene Expression Data Identifies Novel Gene Candidates in Gastric Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;13(12):2233. doi: 10.3390/genes13122233. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kheirelseid E.A.H., Miller N., Kerin M.J. Molecular biology of colorectal cancer: Review of the literature. Am. J. Mol. Biol. 2013;3:72–80. doi: 10.4236/ajmb.2013.32010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

