Progress in the Field of Micro-Electrocorticography
- PMID: 30658503
- PMCID: PMC6356841
- DOI: 10.3390/mi10010062
Progress in the Field of Micro-Electrocorticography
Abstract
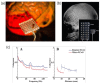
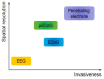
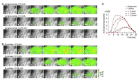
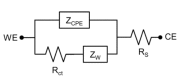
Since the 1940s electrocorticography (ECoG) devices and, more recently, in the last decade, micro-electrocorticography (µECoG) cortical electrode arrays were used for a wide set of experimental and clinical applications, such as epilepsy localization and brain⁻computer interface (BCI) technologies. Miniaturized implantable µECoG devices have the advantage of providing greater-density neural signal acquisition and stimulation capabilities in a minimally invasive fashion. An increased spatial resolution of the µECoG array will be useful for greater specificity diagnosis and treatment of neuronal diseases and the advancement of basic neuroscience and BCI research. In this review, recent achievements of ECoG and µECoG are discussed. The electrode configurations and varying material choices used to design µECoG arrays are discussed, including advantages and disadvantages of µECoG technology compared to electroencephalography (EEG), ECoG, and intracortical electrode arrays. Electrode materials that are the primary focus include platinum, iridium oxide, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT), indium tin oxide (ITO), and graphene. We discuss the biological immune response to µECoG devices compared to other electrode array types, the role of µECoG in clinical pathology, and brain⁻computer interface technology. The information presented in this review will be helpful to understand the current status, organize available knowledge, and guide future clinical and research applications of µECoG technologies.
Keywords: ECoG; brain–computer interface; electrocorticography; electrophysiology; graphene; in vivo imaging; micro-electrocorticography; neural electrode array; neural interfaces; tissue response; µECoG.
Conflict of interest statement
Multiple authors have financial or intellectual property interests in technologies that are described in this review or in the more general area of neuroengineering. J.C.W., D.-W.P., M.S., and Z.M. all have patents on technology described in this review. J.C.W. has an equity interest in NeuroOne Medical (Minnetonka, MN) and NeuroNexus (Ann Arbor, MI), companies that manufacture microfabricated electrode arrays for research and clinical applications.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

