Preventive effects of a novel herbal mixture on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in BALB/C mice
- PMID: 30658631
- PMCID: PMC6339437
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2426-z
Preventive effects of a novel herbal mixture on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in BALB/C mice
Abstract
Background: A combination of parts of Cornus officinalis, Rosa multiflora, Lespedeza bicolor, Platycladus orientalis, and Castanea crenata is commonly used for alleviating inflammatory skin disorders. Therefore, this study was carried out to evaluate the in vitro and in vivo preventive effects of a novel herbal formula made from the five plants (C2RLP) against atopic dermatitis in BALB/C mice.
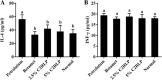
Methods: Mice were allocated into five groups (n = 8) including, control (Normal, petrolatum, and betamethasone treated) and treatment groups (treated with 2.5 and 5% C2RLP ointment). Atopic lesion was induced by applying 1-Chloro-2, 4-dinitrobenzene to the dorsal thoracic area of mice. Macroscopical and histological evaluations were performed to determine the effects of treatment on the progress of the skin lesions. The effects of treatment on the production and release of interleukins, interferon -ϒ, nitrite, prostaglandin E2, thymus and activation-receptor chemokine, and β-hexosaminidase were evaluated and comparisons were made between groups. In addition, the chemical compounds present in C2RLP were identified by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry.
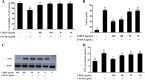
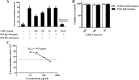
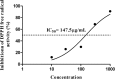
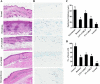
Results: Topical application of C2RLP reduced the dermatitis score and suppressed histopathological changes in mice. Treatment significantly reduced (P < 0.05) plasma IL-4 level, the production of nitrite, prostaglandin E2, and thymus and activation-receptor chemokine production. The lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS-mRNA expression in RAW 264.7 cells was also suppressed by high concentrations of C2RLP. In addition, C2RLP showed an inhibitory effect against DPPH free radical (IC50 = 147.5 μg/ml) and β-hexosaminidase release (IC50 = 179.5 μg/ml). Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry analysis revealed the presence of various compounds, including loganin, ellagic acid, and kaempferol 3-glucoside.
Conclusion: Down-regulation of T- helper 2 cellular responses and suppression of inflammatory mediators contributed to the protective effects of C2RLP from atopic dermatitis in BALB/C mice.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Inflammation; Mice; Skin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Experimental procedures were carried out according to the international guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. The experiment was approved by the Institutional animal care and use committee, Kyungpook National University, Republic of Korea (Approval number: KNU 2016–120).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy and action mechanisms of a Chinese herbal formula on experimental models of atopic dermatitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jun 28;274:114021. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114021. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33716079
-
Topical application of Rosa multiflora root extract improves atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by mite antigen in NC/Nga mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(1):178-83. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b13-00619. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014. PMID: 24389494
-
Combretum quadrangulare Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions through Modulation of MAPK Signaling in BALB/c Mice.Molecules. 2020 Apr 24;25(8):2003. doi: 10.3390/molecules25082003. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32344690 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Role of Nitric Oxide in Cutaneous Inflammation.Inflammation. 2022 Jun;45(3):949-964. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01615-8. Epub 2022 Jan 30. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 35094214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal plants used in treatment of inflammatory skin diseases.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013 Jun;30(3):170-7. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2013.35620. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013. PMID: 24278070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erigeron annuus Extract Improves DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in a Mouse Model via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 3;16(3):451. doi: 10.3390/nu16030451. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38337735 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-atopic dermatitis effects of Parasenecio auriculatus via simultaneous inhibition of multiple inflammatory pathways.BMB Rep. 2022 Jun;55(6):275-280. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022.55.6.144. BMB Rep. 2022. PMID: 35168697 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Obesity Effects of Combined Cornus officinalis and Ribes fasciculatum Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Male Mice.Animals (Basel). 2021 Nov 8;11(11):3187. doi: 10.3390/ani11113187. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827919 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a complex mixture prepared from agrimonia, houttuynia, licorice, peony, and phellodendron on human skin cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 17;10(1):22132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79301-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33335246 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Ulmus davidiana and Cornus officinalis Extracts on Osteoporotic Bone Loss In Vitro and In Vivo.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Mar 23;58(4):466. doi: 10.3390/medicina58040466. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35454305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leung DYM, Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2003:151–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

