Association between severity of periodontitis and clinical activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a case-control study
- PMID: 30658685
- PMCID: PMC6339403
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1808-z
Association between severity of periodontitis and clinical activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a case-control study
Abstract
Background: A high prevalence of periodontitis has been reported in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, although the strength of this association, its temporal link and the possible relationship between the severity of periodontitis and RA disease activity remain unclear. The objective of this work was to investigate whether periodontitis is associated with RA and whether periodontitis severity is linked to RA disease activity.
Methods: This case-control study included 187 patients diagnosed with RA and 157 control patients without inflammatory joint disease. RA disease activity and severity were evaluated by the Disease Activity Score 28, the Simplified Disease Activity Index, the Clinical Disease Activity Index, rheumatoid factor, anti-citrullinated protein antibody titers, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, presence of extra-articular manifestations and type of RA therapy. Exposure severity was assessed by the following periodontal parameters: plaque index, bleeding on probing, probing pocket depth and clinical attachment levels. Sociodemographic variables and comorbidities were evaluated as confounding variables. Outcome and exposure variables were compared by both parametric and nonparametric tests, and possible associations were assessed through regression analysis with a calculation for the adjusted odds ratio (OR).
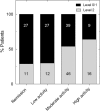
Results: A significant association was demonstrated between periodontitis and RA with an adjusted OR of 20.57 (95% CI 6.02-70.27, p < 0.001). Compared with controls, all parameters related to periodontal status (plaque index, bleeding on probing, probing pocket depth and clinical attachment levels) were significantly worse in RA patients (p < 0.001). Periodontitis severity was significantly associated with RA disease activity (p < 0.001), showing in an ordinal logistic regression model an association between periodontal severity and disease activity with an adjusted OR of 2.66 (95% CI 1.24-5.74, p = 0.012).
Conclusion: A significant association was demonstrated between periodontitis and RA, independent of other confounders. This association was more evident in patients with pronounced periodontal disease and higher RA disease activity.
Keywords: Disease activity; Periodontitis; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by an independent ethics committee and institutional review board from Hospital Universitario de Canarias (Spain), and all subjects provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
In this manuscript individual patient data are not presented.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and severity of periodontitis in Indonesian patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Periodontol. 2013 Aug;84(8):1067-74. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110321. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Periodontol. 2013. PMID: 23075431
-
Periodontal and hematological characteristics associated with aggressive periodontitis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis.J Periodontol. 2006 Feb;77(2):280-8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.050051. J Periodontol. 2006. PMID: 16460255
-
Association between periodontitis and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a cross-sectional study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Feb 13;22(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-2121-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32054521 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a bidirectional association between rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Jun;50(3):414-422. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.01.009. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 32113837
-
Influence of anti-rheumatic agents on the periodontal condition of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Periodontal Res. 2021 Dec;56(6):1099-1115. doi: 10.1111/jre.12925. Epub 2021 Sep 12. J Periodontal Res. 2021. PMID: 34514591
Cited by
-
Associations of periodontal status in periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis patients.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021 Apr;51(2):124-134. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2006060303. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33913635 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into inflammatory osteoclast precursors as therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis.Bone Res. 2023 May 22;11(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00257-w. Bone Res. 2023. PMID: 37217496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porphyromonas Gingivalis in the Development of Periodontitis: Impact on Dysbiosis and Inflammation.Arch Razi Inst. 2022 Oct 31;77(5):1539-1551. doi: 10.22092/ARI.2021.356596.1875. eCollection 2022 Oct. Arch Razi Inst. 2022. PMID: 37123122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of pathogens on host genome and epigenome in development of head and neck cancer.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Nov;6(11):e1846. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1846. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 37322598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
rs2476601 in PTPN22 gene in rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis-a possible interface?J Transl Med. 2020 Oct 15;18(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02548-w. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33059697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rakieh C, Nam JL, Hunt L, Hensor EM, Das S, Bissell LA, et al. Predicting the development of clinical arthritis in anti-CCP positive individuals with non-specific musculoskeletal symptoms: a prospective observational cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1659–1666. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205227. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

