Analysis of a structured intronic region of the LMP2 pre-mRNA from EBV reveals associations with human regulatory proteins and nuclear actin
- PMID: 30658689
- PMCID: PMC6339298
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-019-4070-1
Analysis of a structured intronic region of the LMP2 pre-mRNA from EBV reveals associations with human regulatory proteins and nuclear actin
Abstract
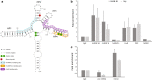
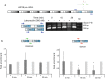
Objective: The pre-mRNA of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP2 (latent membrane protein 2) has a region of unusual RNA structure that partially spans two consecutive exons and the entire intervening intron; suggesting RNA folding might affect splicing-particularly via interactions with human regulatory proteins. To better understand the roles of protein associations with this structured intronic region, we undertook a combined bioinformatics (motif searching) and experimental analysis (biotin pulldowns and RNA immunoprecipitations) of protein binding.
Result: Characterization of the ribonucleoprotein composition of this region revealed several human proteins as interactors: regulatory proteins hnRNP A1 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1), hnRNP U, HuR (human antigen R), and PSF (polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-associated splicing factor), as well as, unexpectedly, the cytoskeletal protein actin. Treatment of EBV-positive cells with drugs that alter actin polymerization specifically showed marked effects on splicing in this region. This suggests a potentially novel role for nuclear actin in regulation of viral RNA splicing.
Keywords: Actin; EBV; Epstein–Barr virus; Herpes virus; HuR; LMP2; PSF; RNA; Splicing; hnRNP A1; hnRNP U.
Figures
References
-
- Glaser SL, Lin RJ, Stewart SL, Ambinder RF, Jarrett RF, Brousset P, Pallesen G, Gulley ML, Khan G, O’Grady J, et al. Epstein–Barr virus-associated Hodgkin’s disease: epidemiologic characteristics in international data. Int J Cancer. 1997;70(4):375–382. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19970207)70:4<375::AID-IJC1>3.0.CO;2-T. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

