Simultaneous extraction of mRNA and microRNA from whole blood stabilized in tempus tubes
- PMID: 30658701
- PMCID: PMC6339331
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-019-4087-5
Simultaneous extraction of mRNA and microRNA from whole blood stabilized in tempus tubes
Abstract
Objective: Studies of mRNA and miRNA expression profiling increasingly use stabilized whole blood. Commercial RNA extraction kits do not provide information about the simultaneous recovery of both mRNA and miRNA. This study evaluated yield, quality, integrity and representation of mRNA and miRNA from whole blood stabilized in Tempus tubes using three RNA extraction kits; two filter-based (Tempus and Norgen) and one bead-based (MagMax; manual vs. semi-automated, and with and without DNase treatment).
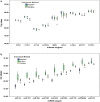
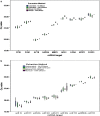
Results: All RNA extraction kits and methods resulted in similar yields of mRNA (total RNA yield, quality, integrity and representation) whereas there were differences in yields of miRNA. MagMax, either manual or semi-automated, with or without DNase treatment, yielded 1.6-2.2-fold more miRNA than Tempus and Norgen kits. In addition, MagMax and Norgen methods gave greater than 12-fold more and 3.3-fold less enrichment of specific miRNA targets, respectively, in comparison to Tempus extraction reagents. This study identified MagMax kit for simultaneous recovery of both mRNA and miRNA from whole blood collected in Tempus tubes.
Keywords: Biobanks; RNA extraction; Stabilized whole blood; Tempus tubes; mRNA and miRNA representation.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

