Clusterin Impairs Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity and Adipocyte Clusterin Associates With Cardiometabolic Risk
- PMID: 30659075
- PMCID: PMC6385696
- DOI: 10.2337/dc18-0870
Clusterin Impairs Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity and Adipocyte Clusterin Associates With Cardiometabolic Risk
Abstract
Objective: Components of the adipose tissue (AT) extracellular matrix (ECM) are recently discovered contributors to obesity-related cardiometabolic disease. We identified increased adipocyte expression of ECM-related clusterin (apolipoprotein J) in obese versus lean women by microarray. Our objective was to determine 1) whether subcutaneous AT adipocyte (SAd) clusterin and serum clusterin are associated with insulin resistance (IR) and known markers of cardiometabolic risk and 2) how clusterin may contribute to increased risk.
Research design and methods: We validated increased clusterin expression in adipocytes from a separate group of 18 lean and 54 obese individuals. The relationship of clusterin gene expression and plasma clusterin with IR, cardiovascular biomarkers, and risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) was then determined. Further investigations in human cultured cells and in aged LDLR-/- mice prone to development of obesity-associated complications were performed.
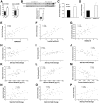
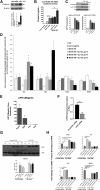
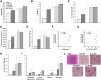
Results: SAd clusterin correlated with IR, multiple CVD biomarkers, and CVD risk, independent of traditional risk factors. Circulating human clusterin exhibited similar associations. In human adipocytes, palmitate enhanced clusterin secretion, and in human hepatocytes, clusterin attenuated insulin signaling and APOA1 expression and stimulated hepatic gluconeogenesis. LRP2 (megalin), a clusterin receptor, highly expressed in liver, mediated these effects, which were inhibited by LRP2 siRNA. In response to Western diet feeding, an increase in adipocyte clusterin expression was associated with a progressive increase in liver fat, steatohepatitis, and fibrosis in aged LDLR-/- mice.
Conclusions: Adipocyte-derived clusterin is a novel ECM-related protein linking cardiometabolic disease and obesity through its actions in the liver.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001;24:683–689 - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 1991;14:173–194 - PubMed
-
- Graßmann S, Wirsching J, Eichelmann F, Aleksandrova K. Association between peripheral adipokines and inflammation markers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2017;25:1776–1785 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

