Hepatitis B virus X protein-induced SH2 domain-containing 5 (SH2D5) expression promotes hepatoma cell growth via an SH2D5-transketolase interaction
- PMID: 30659097
- PMCID: PMC6442033
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005739
Hepatitis B virus X protein-induced SH2 domain-containing 5 (SH2D5) expression promotes hepatoma cell growth via an SH2D5-transketolase interaction
Abstract
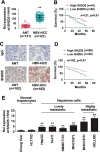
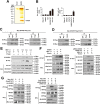
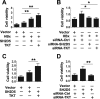
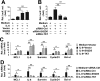
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) critically contributes to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanisms by which HBx promotes HCC remain unclear. In the present study, using a combination of gene expression profiling and immunohistochemistry, we found higher levels of SH2 domain-containing 5 (SH2D5) in liver tissue from HBV-associated HCC (HBV-HCC) patients than in adjacent nontumor tissues. Moreover, HBV infection elevated SH2D5 levels, and we observed that HBx plays an important role in SH2D5 induction. We also found that HBx triggers SH2D5 expression through the NF-κB and c-Jun kinase pathways. Employing SH2D5 overexpression or knockdown, we further demonstrate that SH2D5 promotes HCC cell proliferation both in vitro and in vivo While investigating the mechanism of SH2D5-mediated stimulation of HCC cell proliferation, we noted that HBV induces SH2D5 binding to transketolase (TKT), a pentose phosphate pathway enzyme, thereby promoting an interaction between and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Furthermore, HBx stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation at Tyr-705 and promoted the activity and downstream signaling pathway of STAT3 via the SH2D5-TKT interaction. Taken together, our results suggest that SH2D5 is an HBV-induced protein capable of binding to TKT, leading to induction of HCC cell proliferation.
Keywords: HBV X protein; HBV-associated HCC; IL-6-STAT3 signaling; SH2D5; cancer biology; cell migration; hepatitis B virus (HBV, Hep B); inflammation; interleukin 6 (IL-6); transketolase.
© 2019 Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes interleukin-7 receptor expression via NF-κB and Notch1 pathway to facilitate proliferation and migration of hepatitis B virus-related hepatoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 7;35(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0448-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27821177 Free PMC article.
-
RPS3a over-expressed in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma enhances the HBx-induced NF-κB signaling via its novel chaperoning function.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022258. Epub 2011 Aug 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21857917 Free PMC article.
-
HBX protein promotes LASP-1 expression through activation of c-Jun in human hepatoma cells.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):7279-7291. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26560. Epub 2018 Mar 30. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29600594
-
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10238-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2014 Apr 10;345(2):216-22. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Aug 25. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 23981576 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hepatitis B Virus Interactome: A Comprehensive Overview.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 16;12:724877. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.724877. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34603251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The First Yarrowia lipolytica Yeast Models Expressing Hepatitis B Virus X Protein: Changes in Mitochondrial Morphology and Functions.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 10;10(9):1817. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091817. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144419 Free PMC article.
-
Helicid Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Apoptosis of C6 Cells by Regulating SH2D5 DNA Methylation via the CytC/Caspase9/Caspase3 Signaling Pathway.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jan 31;2022:9242827. doi: 10.1155/2022/9242827. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9858510. doi: 10.1155/2023/9858510. PMID: 35173561 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Prognostic values of transketolase family genes in ovarian cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):4845-4857. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10818. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31611995 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Pattern-Recognition Receptor Signaling by HBX During Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 17;13:829923. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.829923. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35251017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen S., Dong Z., Yang P., Wang X., Jin G., Yu H., Chen L., Li L., Tang L., Bai S., Yan H., Shen F., Cong W., Wen W., and Wang H. (2017) Hepatitis B virus X protein stimulates high mobility group box 1 secretion and enhances hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Lett. 394, 22–32 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang P., Li Q. J., Feng Y., Zhang Y., Markowitz G. J., Ning S., Deng Y., Zhao J., Jiang S., Yuan Y., Wang H. Y., Cheng S. Q., Xie D., and Wang X. F. (2012) TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 22, 291–303 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.07.023 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu D., Cui L., Wang Y., Yang G., He J., Hao R., Fan C., Qu M., Liu Z., Wang M., Chen L., Li H., and Guo D. (2016) Hepatitis B e antigen and its precursors promote the progress of hepatocellular carcinoma by interacting with NUMB and decreasing p53 activity. Hepatology 64, 390–404 10.1002/hep.28594 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

