Genotype tailored treatment of mild symptomatic acid reflux in children with uncontrolled asthma (GenARA): Rationale and methods
- PMID: 30659924
- PMCID: PMC7039713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2019.01.009
Genotype tailored treatment of mild symptomatic acid reflux in children with uncontrolled asthma (GenARA): Rationale and methods
Abstract
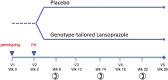
Asthma causes enormous suffering and cost for children in the US and around the world [1-3]. Co-morbid gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) makes asthma management more difficult due to increased symptoms. Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) drugs are effective at improving to GERD symptoms, however they have demonstrated only modest and variable effects on asthma control in the setting of co-morbid GERD. Importantly, PPI metabolism and efficacy depend on CYP2C19 genotype. The Genotype Tailored Treatment of Symptomatic Acid Reflux in Children with Uncontrolled Asthma (GenARA) study is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to determine if genotype-tailored PPI dosing improves asthma symptoms among children with inadequately controlled asthma and GERD symptoms. This study has an innovative design to both assess the efficacy of genotype-tailored PPI dosing and perform pharmacokinetic modeling of the oral PPI Lansoprazole. Children ages 6-17 years old with clinician-diagnosed asthma and mild GERD symptoms will submit a saliva sample for CYP2C19 genotyping. Participants will undergo a two-step randomization to: (1) genotype-tailored versus conventional dosing of open-label oral lansoprazole for pharmacokinetic modeling, and (2) genotype-tailored lansoprazole daily versus placebo for 24 weeks to determine the effect of genotype-tailored PPI dosing on asthma control. Measures of asthma control, spirometry, and nasal washes during acute illnesses will be collected at 8-week intervals throughout the study. GenARA will better define the effects of CYP2C19 genotype on the dose response of lansoprazole in children and adolescents and assess if a novel dosing regimen improves GERD and asthma control.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Akinbami L.J. Trends in asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality in the United States, 2001-2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2012;94:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Swallen K.C. Overweight, obesity, and health-related quality of life among adolescents: the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Pediatrics. 2005;115(2):340–347. - PubMed
-
- Franciosi J.P. Association between CYP2C19 extensive metabolizer phenotype and childhood anti-reflux surgery following failed proton pump inhibitor medication treatment. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018;177(1):69–77. - PubMed