Single-molecule FRET method to investigate the dynamics of transcription elongation through the nucleosome by RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 30660864
- PMCID: PMC6589119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.01.009
Single-molecule FRET method to investigate the dynamics of transcription elongation through the nucleosome by RNA polymerase II
Abstract
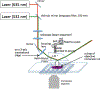
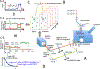
Transcription elongation through the nucleosome is a precisely coordinated activity to ensure timely production of RNA and accurate regulation of co-transcriptional histone modifications. Nucleosomes actively participate in transcription regulation at various levels and impose physical barriers to RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) during transcription elongation. Despite its high significance, the detailed dynamics of how RNAPII translocates along nucleosomal DNA during transcription elongation and how the nucleosome structure dynamically conforms to the changes necessary for RNAPII progression remain poorly understood. Transcription elongation through the nucleosome is a complex process and investigating the changes of the nucleosome structure during this process by ensemble measurements is daunting. This is because it is nearly impossible to synchronize elongation complexes within a nucleosome or a sub-nucleosome to a designated location at a high enough efficiency for desired sample homogeneity. Here we review our recently developed single-molecule FRET experimental system and method that has fulfilled this deficiency. With our method, one can follow the changes in the structure of individual nucleosomes during transcription elongation. We demonstrated that this method enables the detailed measurements of the kinetics of transcription elongation through the nucleosome and its regulation by a transcription factor, which can be easily extended to investigations of the roles of environmental variables and histone post-translational modifications in regulating transcription elongation.
Keywords: Nucleosome; RNA polymerase II; Single-molecule FRET; Transcription elongation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


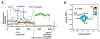
Similar articles
-
The elongation factor Spt4/5 regulates RNA polymerase II transcription through the nucleosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 20;45(11):6362-6374. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx220. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28379497 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into nucleosome transcription by RNA polymerase II with elongation factors.Science. 2019 Feb 15;363(6428):744-747. doi: 10.1126/science.aav8912. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Science. 2019. PMID: 30733384
-
Spt4 facilitates the movement of RNA polymerase II through the +2 nucleosomal barrier.Cell Rep. 2021 Sep 28;36(13):109755. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109755. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34592154 Free PMC article.
-
Negotiating the nucleosome: factors that allow RNA polymerase II to elongate through chromatin.Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;85(4):426-34. doi: 10.1139/O07-054. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17713578 Review.
-
Chromatin Transcription Elongation - A Structural Perspective.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168845. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168845. Epub 2024 Oct 29. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39476950 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Histone H2B Ubiquitylations and H3K79me3 on Transcription Elongation.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Mar 17;18(3):537-548. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00887. Epub 2023 Mar 1. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 36857155 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosome Dynamics during Transcription Elongation.ACS Chem Biol. 2020 Dec 18;15(12):3133-3142. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00617. Epub 2020 Dec 2. ACS Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 33263994 Free PMC article.
-
Methods to investigate nucleosome structure and dynamics with single-molecule FRET.Methods. 2023 Jul;215:17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 May 24. Methods. 2023. PMID: 37236433 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Molecule Techniques to Study Chromatin.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 5;9:699771. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.699771. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34291054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Development in Biomedical Applications of Oligonucleotides with Triplex-Forming Ability.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;15(4):858. doi: 10.3390/polym15040858. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36850142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cramer P, Bushnell DA, Fu J, Gnatt AL, Maier-Davis B, Thompson NE, Burgess RR, Edwards AM, David PR, Kornberg RD, Architecture of RNA polymerase II and implications for the transcription mechanism, Science (New York, N.Y.), 288 (2000) 640–649. - PubMed
-
- Kireeva ML, Hancock B, Cremona GH, Walter W, Studitsky VM, Kashlev M, Nature of the nucleosomal barrier to RNA polymerase II, Mol Cell, 18 (2005) 97–108. - PubMed
-
- Sydow JF, Brueckner F, Cheung AC, Damsma GE, Dengl S, Lehmann E, Vassylyev D, Cramer P, Structural basis of transcription: mismatch-specific fidelity mechanisms and paused RNA polymerase II with frayed RNA, Mol Cell, 34 (2009) 710–721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

