Effects of diet before endurance exercise on hepcidin response in young untrained females
- PMID: 30661331
- PMCID: PMC6343765
- DOI: 10.20463/jenb.2018.0030
Effects of diet before endurance exercise on hepcidin response in young untrained females
Abstract
Purpose: We examined the effects of diet before endurance exercise on hepcidin response in young untrained females.
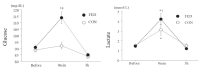
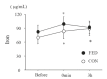
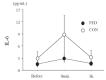
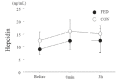
Methods: Ten young untrained females [age: 20.6 ± 0.8 y, height: 157.5 ± 1.0 cm, weight: 54.4 ± 1.5 kg, and maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max): 35.9 ± 1.1 mL/kg/min] were involved in two experimental conditions with a crossover design. The two conditions were separated by approximately 1 month, and each condition was performed during the follicular phase. Subjects completed 60 min of pedaling at 65% of VO2max after consuming a meal (FED) or not consuming a meal (CON). Blood samples were collected before, immediately after, and 3 h after exercise.
Results: Serum ferritin levels before exercise did not differ between the two conditions (P > 0.05). Blood glucose and lactate levels were significantly elevated immediately after exercise only under the FED condition (P < 0.05). Serum iron levels were significantly elevated after exercise under both conditions. However, the plasma interleukin-6 and serum hepcidin levels were not significantly different 3 h after exercise under either condition (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Consuming a meal before endurance exercise at moderate intensity did not affect exercise-induced hepcidin elevation in young untrained females.
Keywords: Iron metabolism.
©2018 The Korean Society for Exercise Nutrition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Resistance exercise causes greater serum hepcidin elevation than endurance (cycling) exercise.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 27;15(2):e0228766. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228766. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32106271 Free PMC article.
-
Heat acclimation does not attenuate hepcidin elevation after a single session of endurance exercise under hot condition.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022 Aug;122(8):1965-1974. doi: 10.1007/s00421-022-04974-8. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35674827 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of post-exercise carbohydrate ingestion: influence on IL-6 and hepcidin responses.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015 Oct;115(10):2215-22. doi: 10.1007/s00421-015-3202-0. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26084589
-
Postexercise serum hepcidin response to repeated sprint exercise under normoxic and hypoxic conditions.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018 Mar;43(3):221-226. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2017-0418. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018. PMID: 28961407
-
Effects of an Acute Exercise Bout on Serum Hepcidin Levels.Nutrients. 2018 Feb 14;10(2):209. doi: 10.3390/nu10020209. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29443922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inter-individual variation in SpO2 during endurance exercise in hypoxia does not correlate with endocrine and angiogenic growth factor responses.Physiol Rep. 2025 Feb;13(3):e70221. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70221. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39924721 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Influencing the Hepcidin Response to Exercise: An Individual Participant Data Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2023 Oct;53(10):1931-1949. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01874-5. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37347443
References
-
- Sinclar LM, Hinton PS. Prevalence of iron deficiency with and without anemia in recreationally active men and women. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105:975–8. - PubMed
-
- Babić Z, Papa B, Sikirika-Bosnjaković M, Prkacin I, Misigoj-Duraković M, Katicić M. Occult gastrointestinal bleeding in rugby players. J Sports Med Phy Fitness. 2001;41:399–402. - PubMed
-
- Lampe JW, Slavin JL, Apple FS. Poor iron status of women runners for marathon. Int J Sports Med. 1986;7:111–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

