Integrated Signaling Pathways Mediate Bordetella Immunomodulation, Persistence, and Transmission
- PMID: 30661570
- PMCID: PMC6342287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.09.010
Integrated Signaling Pathways Mediate Bordetella Immunomodulation, Persistence, and Transmission
Abstract
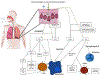
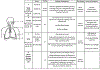
The mammalian immune system includes a sophisticated array of antimicrobial mechanisms. However, successful pathogens have developed subversive strategies to detect, modulate, and/or evade immune control and clearance. Independent disciplines study host immunology and bacterial pathogenesis, but interkingdom signaling between bacteria and host during natural infection remains poorly understood. An efficient natural host infection system has revealed complex communication between Bordetella spp. and mice, identified novel regulatory mechanisms, and demonstrated that bordetellae can respond to microenvironment and inflammatory status cues. Understanding these bacterial signaling pathways and their complex network that allows precisely timed expression of numerous immunomodulatory factors will serve as a paradigm for other organisms lacking such a powerful experimental infection system. VIDEO ABSTRACT.
Keywords: Bordetella spp.; immune response; immunomodulators; pathogenesis; signaling.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancement of immune response against Bordetella spp. by disrupting immunomodulation.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 30;9(1):20261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56652-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31889098 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils as drivers of bacterial immunomodulation and persistence.Infect Immun. 2024 Sep 10;92(9):e0017524. doi: 10.1128/iai.00175-24. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 39007622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulation as a Novel Strategy for Prevention and Treatment of Bordetella spp. Infections.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 13;10:2869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02869. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bordetella filamentous hemagglutinin plays a critical role in immunomodulation, suggesting a mechanism for host specificity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Dec 20;102(51):18578-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507910102. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16339899 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling systems-level regulation of host immune responses.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Jun;3(6):e109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030109. Epub 2007 Apr 30. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17559300 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhancement of immune response against Bordetella spp. by disrupting immunomodulation.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 30;9(1):20261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56652-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31889098 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Bordetella pertussis and its adaptation to its strictly human host.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2608-2632. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1980987. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34590541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generating enhanced mucosal immunity against Bordetella pertussis: current challenges and new directions.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 21;14:1126107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1126107. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36895562 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils as drivers of bacterial immunomodulation and persistence.Infect Immun. 2024 Sep 10;92(9):e0017524. doi: 10.1128/iai.00175-24. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 39007622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupting Bordetella Immunosuppression Reveals a Role for Eosinophils in Coordinating the Adaptive Immune Response in the Respiratory Tract.Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 17;8(11):1808. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111808. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33212993 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

