Human Semaphorin 3 Variants Link Melanocortin Circuit Development and Energy Balance
- PMID: 30661757
- PMCID: PMC6370916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.009
Human Semaphorin 3 Variants Link Melanocortin Circuit Development and Energy Balance
Abstract
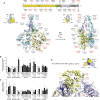
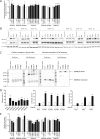
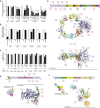
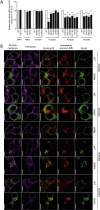
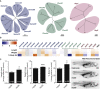
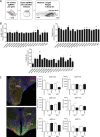
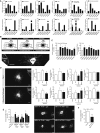
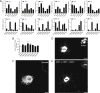
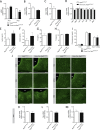
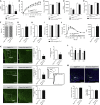
Hypothalamic melanocortin neurons play a pivotal role in weight regulation. Here, we examined the contribution of Semaphorin 3 (SEMA3) signaling to the development of these circuits. In genetic studies, we found 40 rare variants in SEMA3A-G and their receptors (PLXNA1-4; NRP1-2) in 573 severely obese individuals; variants disrupted secretion and/or signaling through multiple molecular mechanisms. Rare variants in this set of genes were significantly enriched in 982 severely obese cases compared to 4,449 controls. In a zebrafish mutagenesis screen, deletion of 7 genes in this pathway led to increased somatic growth and/or adiposity demonstrating that disruption of Semaphorin 3 signaling perturbs energy homeostasis. In mice, deletion of the Neuropilin-2 receptor in Pro-opiomelanocortin neurons disrupted their projections from the arcuate to the paraventricular nucleus, reduced energy expenditure, and caused weight gain. Cumulatively, these studies demonstrate that SEMA3-mediated signaling drives the development of hypothalamic melanocortin circuits involved in energy homeostasis.
Keywords: AgRP; Neuropilins; Plexins; Pomc; Semaphorin 3s; hypothalamus; obesity.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Development of melanocortin circuits.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Apr;15(4):191. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0171-0. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30710099 No abstract available.
-
Axon Guidance Molecules Implicated in Early-Onset Obesity.Trends Neurosci. 2019 Jul;42(7):439-440. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Trends Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30981443
References
-
- Balthasar N., Coppari R., McMinn J., Liu S.M., Lee C.E., Tang V., Kenny C.D., McGovern R.A., Chua S.C., Jr., Elmquist J.K., Lowell B.B. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2004;42:983–991. - PubMed
-
- Bouret S.G., Draper S.J., Simerly R.B. Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science. 2004;304:108–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RG/18/13/33946/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 17721/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- BTRU-2014-10024/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 203141/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RG/10/17/28553/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 098497/Z/12/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0900554/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 100574/Z/12/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK084142/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00014/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK102780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- WT098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- C375/A17721/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 099038/Z/12/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK118401/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12012/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M000141/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S025685/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

