A Prospective Study on Operation Theater Utilization Time and Most Common Causes of Delays and Cancellations of Scheduled Surgeries in a 1000-Bedded Tertiary Care Rural Hospital with a View to Optimize the Utilization of Operation Theater
- PMID: 30662110
- PMCID: PMC6319069
- DOI: 10.4103/aer.AER_132_18
A Prospective Study on Operation Theater Utilization Time and Most Common Causes of Delays and Cancellations of Scheduled Surgeries in a 1000-Bedded Tertiary Care Rural Hospital with a View to Optimize the Utilization of Operation Theater
Abstract
Background: The operation theater (OT) complex is a costly component of a hospital budget expenditure. This area of hospital activity requires maximum utilization to ensure optimum cost benefit. To achieve a high level of utilization in the OT, it is necessary to efficiently coordinate number of activities and personnel.
Methods: This study was conducted in a 1000-bedded tertiary care teaching hospital in rural maharashtra over aperiod of two months. The OT complex consists of eight major OTs. Normal working hours for routine scheduled cases on all working days except Sundays and public holidays.
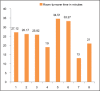
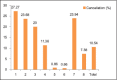
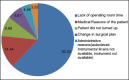
Results: Total study period consisted of 96 working days. There were a total of eight OT tables of various specialties, and parameters were observed during the routine hours excluding Sundays and holidays. The total procedure time was maximum for ENT followed by orthopedics and least for obstetrics. Room turnover time was maximum for obstetrics followed by general and oncosurgery. Case delays were maximum in general surgery and least for ophthalmology. The most common reason for delay in starting the operation table was patient getting shifted late from the ward and administrative causes. The most prominent reasons for cancellation were lack of operating room time followed by medical reasons of the patient.
Conclusion: We concluded that most of the causes of delays and cancellations of surgeries were avoidable with proper preoperative planning and optimization of patients and resources and good communication between surgeon anesthesiologists and the nursing staff.
Keywords: Cancellations; operation theatre; rescheduling of surgeries; utilization.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An analysis of time utilization and cancellations of scheduled cases in the main operation theater complex of a tertiary care teaching institute of North India.J Postgrad Med. 2015 Jan-Mar;61(1):3-8. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.147009. J Postgrad Med. 2015. PMID: 25511210 Free PMC article.
-
Causes of cancellations on the day of surgery at a Tertiary Teaching Hospital.BMC Health Serv Res. 2016 Jul 13;16:259. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1475-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016. PMID: 27412041 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Time Utilization in the Operating Theater and Factors Contributing to Delays in Scheduled Surgeries.Cureus. 2025 May 7;17(5):e83671. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83671. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40486376 Free PMC article.
-
Audit of the Functioning of the Elective Neurosurgical Operation Theater in India: A Prospective Study and Review of Literature.World Neurosurg. 2015 Aug;84(2):345-50. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2015.03.031. Epub 2015 Apr 10. World Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25865437 Review.
-
Cancellation of Surgeries: Integrative Review.J Perianesth Nurs. 2019 Feb;34(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jopan.2017.09.012. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Perianesth Nurs. 2019. PMID: 29678319 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparative study of key quality performance indicators in anesthesia and surgery in operation theatre at a tertiary care hospital in Rishikesh.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Mar;40(1):147-153. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_33_22. Epub 2024 Mar 14. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38666178 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Elective Neurosurgical Theater Utilization Audit in Pakistan: Problems in a Public Tertiary Care Hospital and Proposed Solutions from Lower-Middle-Income Country.Asian J Neurosurg. 2022 Jun 10;17(1):58-67. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1749110. eCollection 2022 Mar. Asian J Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35873839 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgery Cancellations After Patients are Taken to the Operating Room: A Prospective, Cross-Sectional Study.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):14-21. doi: 10.4274/TJAR.2024.231454. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2024. PMID: 38414170 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Artificial Intelligence for Orthopedic Surgical Backlogs Such as the One Following the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review.JB JS Open Access. 2024 Sep 19;9(3):e24.00100. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.24.00100. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. JB JS Open Access. 2024. PMID: 39301194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgical Cancellations: Findings from a Rural Tertiary Hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 15;11(2):270. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11020270. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36673638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vinukondaiah K, Ananthakrishnan N, Ravishankar M. Audit of operation theatre utilization in general surgery. Natl Med J India. 2000;13:118–21. - PubMed
-
- Schofield WN, Rubin GL, Piza M, Lai YY, Sindhusake D, Fearnside MR, et al. Cancellation of operations on the day of intended surgery at a major Australian referral hospital. Med J Aust. 2005;182:612–5. - PubMed
-
- Wildner M, Bulstrode C, Spivey J, Carr A, Nugent I. Avoidable causes of cancellation in elective orthopaedic surgery. Health Trends. 1991;23:115–6. - PubMed
-
- Sonal S. Express Health Care: Streamlining. Occup Ther. 2008;2:12.
-
- Sherman HD. Hospital efficiency measurement and evaluation. Empirical test of a new technique. Med Care. 1984;22:922–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous