Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Erector Spinae Plane Block and Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum Block for Postoperative Analgesia in Hip and Proximal Femur Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Feasibility Study
- PMID: 30662115
- PMCID: PMC6319070
- DOI: 10.4103/aer.AER_142_18
Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Erector Spinae Plane Block and Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum Block for Postoperative Analgesia in Hip and Proximal Femur Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Feasibility Study
Abstract
Study objective: Lumbar Erector spinae Plane block (L-ESPB) is a modification of a recently described block. Both L-ESPB and Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum block (QLB-T) have been reported to provide effective postoperative analgesia in hip and proximal femur surgery. Herein, we compare the effectiveness of L-ESPB and QLB-T in providing postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing hip and femur operations.
Design: Double-blinded, prospective, randomized, feasibility study.
Setting: Tertiary university hospital, postoperative recovery room and ward.
Methodology: A total of 72 patients (American Society of Anesthesiology physical status classification II-III) were recruited. After exclusion, 60 patients were allocated to three equal groups (control, L-ESB and QLB-t).
Interventions: Standard multimodal analgesia was performed in the control group while L-ESPB or QLB-T was performed in the block groups.
Measurements: Pain intensity between groups was compared using Numeric Rating Scores. Furthermore, tramadol consumption and additional rescue analgesic requirement was measured.
Results: There was no difference between demographic data or type of surgery. While there was no difference in Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) score at any hour between the block groups; NRS scores at the 1st, 3rd and 6th h, tramadol consumption during the first 12 h and total tramadol consumption, the number of patient required rescue analgesic in 24 h were significantly higher in the control group compared to both block groups.
Conclusion: While L-ESPB and QLB-T have similar effect, they improve analgesia quality in patients undergoing hip and proximal femoral surgery when compared to standard intravenous analgesia regimen.
Keywords: Erector spinae plane block; hip surgery; quadratus lumborum block.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

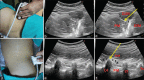
References
-
- Haque M, Fregene T. Fascia iliaca block for hip replacement – Adjuvants and ethics. Anaesthesia. 2017;72:659–60. - PubMed
-
- Forero M, Adhikary SD, Lopez H, Tsui C, Chin KJ. The erector spinae plane block: A novel analgesic technique in thoracic neuropathic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016;41:621–7. - PubMed
-
- Chin KJ, Adhikary S, Sarwani N, Forero M. The analgesic efficacy of pre-operative bilateral erector spinae plane (ESP) blocks in patients having ventral hernia repair. Anaesthesia. 2017;72:452–60. - PubMed
-
- Ueshima H, Otake H. Erector spinae plane block provides effective pain management during pneumothorax surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2017;40:74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

