Initial clinical trial of pins coated with fibroblast growth factor-2-apatite composite layer in external fixation of distal radius fractures
- PMID: 30662242
- PMCID: PMC6324763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2018.12.012
Initial clinical trial of pins coated with fibroblast growth factor-2-apatite composite layer in external fixation of distal radius fractures
Abstract
Background: Pin tract infection and loosening are major complications and challenges in the treatment of fractures by external fixation. To address this issue, we developed titanium pins coated with a fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2)-apatite composite layer. The purpose of this initial clinical trial is to clarify the safety and feasibility of using these pins for the external fixation of distal radius fractures.
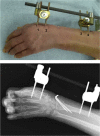
Methods: Unstable, displaced fractures of the distal radius that were medically suitable for external fixation were treated using external fixation pins coated and uncoated with an FGF-2-apatite composite layer. The coated pin group (n = 5) comprised 5 women (average age, 70.4 ± 5.9 years), whereas the uncoated pin group (n = 10) comprised 8 women and 2 men (average age, 64.4 ± 11.7 years). The average duration of external fixation was 40.8 ± 1.3 and 41.6 ± 2.1 days for the coated and uncoated pin groups, respectively.
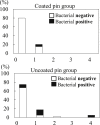
Results: All patients achieved fracture union. One patient in the uncoated group had severe pin tract infection on the day of pin extraction. No pin loosening or difficulty in pin removal was observed in either group. Bacterial growth was present in 5% and 25% of the pin sites in the coated and uncoated groups, respectively (p = 0.059). No adverse events such as tumor formation were observed for more than 2 years after surgery in the coated pin group.
Conclusions: This study clarified the safety and feasibility of using pins coated with an FGF-2-apatite composite layer for the external fixation of distal radius fractures.
Keywords: Apatite; Coating; Distal radius fractures; External fixation; Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2); Initial clinical trial; Safety.
Figures
References
-
- W-Dahl A., Toksvig-Larsen S., Lindstrand A. No difference between daily and weekly pin site care: a randomized study of 50 patients with external fixation. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:704–708. - PubMed
-
- Wassall M.A., Santin M., Isalberti C., Cannas M., Denyer S.P. Adhesion of bacteria to stainless steel and silver-coated orthopedic external fixation pins. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;36:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Moroni A., Faldini C., Marchetti S., Manca M., Consoli V., Giannini S. Improvement of the bone-pin interface strength in osteoporotic bone with use of hydroxyapatite-coated tapered external-fixation pins. A prospective, randomized clinical study of wrist fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:717–721. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura H., Matsuno T., Hashimoto Y., Nakamura T., Mataga I. Comparison of a hydroxyapatite-coated and an anodic oxidized titanium implant for experimentally induced peri-implantitis: macroscopic and novel radiographic evaluations in a canine model. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2015;24:347–355.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

