Ginsenoside Rk1 ameliorates paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through inhibition of inflammation, oxidative stress, nitrative stress and apoptosis
- PMID: 30662289
- PMCID: PMC6323149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.07.003
Ginsenoside Rk1 ameliorates paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through inhibition of inflammation, oxidative stress, nitrative stress and apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Frequent overdose of paracetamol (APAP) has become the major cause of acute liver injury. The present study was designed to evaluate the potential protective effects of ginsenoside Rk1 on APAP-induced hepatotoxicity and investigate the underlying mechanisms for the first time.
Methods: Mice were treated with Rk1 (10 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg) by oral gavage once per d for 7 d. On the 7th d, all mice treated with 250 mg/kg APAP exhibited severe liver injury after 24 h, and hepatotoxicity was assessed.
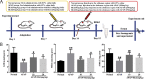
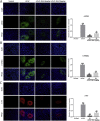
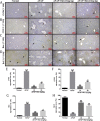
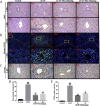
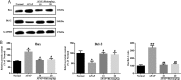
Results: Our results showed that pretreatment with Rk1 significantly decreased the levels of serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1β compared with the APAP group. Meanwhile, hepatic antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase and glutathione, were elevated compared with the APAP group. In contrast, a significant decrease in levels of the lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde was observed in the ginsenoside Rk1-treated group compared with the APAP group. These effects were associated with a significant increase of cytochrome P450 E1 and 4-hydroxynonenal levels in liver tissues. Moreover, ginsenoside Rk1 supplementation suppressed activation of apoptotic pathways by increasing Bcl-2 and decreasing Bax protein expression levels, which was shown using western blotting analysis. Histopathological observation also revealed that ginsenoside Rk1 pretreatment significantly reversed APAP-induced necrosis and inflammatory infiltration in liver tissues. Biological indicators of nitrative stress, such as 3-nitrotyrosine, were also inhibited after pretreatment with Rk1 compared with the APAP group.
Conclusion: The results clearly suggest that the underlying molecular mechanisms in the hepatoprotection of ginsenoside Rk1 in APAP-induced hepatotoxicity may be due to its antioxidation, antiapoptosis, anti-inflammation, and antinitrative effects.
Keywords: APAP-induced hepatotoxicity; anti-apoptosis; anti-inflammation; ginsenoside Rk1; oxidative stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ameliorative Effects and Possible Molecular Mechanism of Action of Black Ginseng (Panax ginseng) on Acetaminophen-Mediated Liver Injury.Molecules. 2017 Apr 21;22(4):664. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040664. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28430162 Free PMC article.
-
Saponins (Ginsenosides) from the Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Ameliorated Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 May 10;65(18):3684-3692. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00610. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28429935
-
Caspase-Mediated Anti-Apoptotic Effect of Ginsenoside Rg5, a Main Rare Ginsenoside, on Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Oct 25;65(42):9226-9236. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03361. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28965396
-
Improved protective effects of American ginseng berry against acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity through TNF-α-mediated caspase-3/-8/-9 signaling pathways.Phytomedicine. 2018 Dec 1;51:128-138. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.234. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466610
-
Anti-TLR4 IgG2 Prevents Acetaminophen-induced Acute Liver Injury through the Toll-like Receptor 4/MAPKs Signaling Pathway in Mice.Curr Mol Med. 2023;23(5):453-469. doi: 10.2174/1566524022666220516141728. Curr Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 35578873
Cited by
-
Natural Products for Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Dec 1;28(23):7901. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237901. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Small Airway Epithelium-Related Hub Genes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022 Nov 30;17:3001-3015. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S377026. eCollection 2022. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022. PMID: 36475041 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rk1 Enhances Chemosensitivity of Gastric Cancer Through Activating the AMPK/mTOR Pathway.Dose Response. 2025 Aug 5;23(3):15593258251349653. doi: 10.1177/15593258251349653. eCollection 2025 Jul-Sep. Dose Response. 2025. PMID: 40771730 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the efficacy and mechanism of action of panax ginseng monomer saponins treat toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 19;13:1022266. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1022266. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36199681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Ginsenoside Rb1, Rg3, Rk1, Rg5, F2, and Compound K from Red Ginseng Extract in Healthy Korean Volunteers.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 24;2022:8427519. doi: 10.1155/2022/8427519. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35111231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun H., Chen L., Zhou W., Hu L., Li L., Tu Q., Chang Y., Liu Q., Sun X., Wu M. The protective role of hydrogen-rich saline in experimental liver injury in mice. J Hepatol. 2011;54:471–480. - PubMed
-
- Dargan P., Jones A. Paracetamol: balancing risk against benefit. QJM. 2002;95:831–832. - PubMed
-
- He M., Zhang S., Jiao Y., Lin X., Huang J., Chen C., Chen Z., Huang R. Effects and mechanisms of rifampin on hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50:3142–3149. - PubMed
-
- Larson A.M. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis. 2007;11:525–548. vi. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

