Management of Osteomyelitis-Induced Massive Tibial Bone Defect by Monolateral External Fixator Combined with Antibiotics-Impregnated Calcium Sulphate: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 30662918
- PMCID: PMC6313967
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9070216
Management of Osteomyelitis-Induced Massive Tibial Bone Defect by Monolateral External Fixator Combined with Antibiotics-Impregnated Calcium Sulphate: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Aim: The present study is aimed at evaluating the effect of combined treatment on massive bone defect using radical debridement, antibiotic calcium sulphate, and monolateral external fixator.
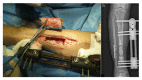
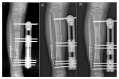
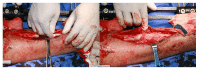
Methods: 35 patients with tibial osteomyelitis received radical debridement, and during surgery antibiotics-impregnated calcium sulphate was used for filling the bone defect. Monolateral external fixator was used to manage the bone defect of average 95 (61-185) cm.
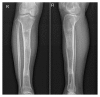
Results: Bone union was achieved in 34 patients (97.1%) with no reinfection. One case was presented with reinfection and further debridement was conducted. The average time for the utility of external fixation was 17 (7-32) months, and external fixation index (EFI) was 1.79 mon/cm. The mean follow-up duration after surgery was 33.7 (21-41) months. 19, 13, and 3 patients got excellent, good, and fair bone results, respectively. Meanwhile, functional results were excellent, good, fair, and poor in 13, 15, 6, and 1 patient. The most common complication was pain (100%) and superficial pin-tract infection (22.8%). Delayed maturation was incurred in 2 patients.
Conclusion: Our study reveals that radical debridement combined with antibiotics-impregnated calcium sulphate can suppress infection, and distraction osteogenesis using monolateral external fixators plays an effective role in managing osteomyelitis-induced massive tibial bone defect.
Figures

References
-
- Sancineto C. F., Barla J. D. Treatment of long bone osteomyelitis with a mechanically stable intramedullar antibiotic dispenser: nineteen consecutive cases with a minimum of 12 months follow-up. The Journal of Trauma—Injury, Infection and Critical Care. 2008;65(6):1416–1420. doi: 10.1097/ta.0b013e31818c6a09. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hutson J. J., Dayicioglu D., Oeltjen J. C., Panthaki Z. J., Armstrong M. B. The treatment of gustilo grade IIIB tibia fractures with application of antibiotic spacer, flap, and sequential distraction osteogenesis. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2010;64(5):541–552. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181cf9fb5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

