STEM CELL THERAPIES, GENE-BASED THERAPIES, OPTOGENETICS, AND RETINAL PROSTHETICS: Current State and Implications for the Future
- PMID: 30664120
- PMCID: PMC6492547
- DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002449
STEM CELL THERAPIES, GENE-BASED THERAPIES, OPTOGENETICS, AND RETINAL PROSTHETICS: Current State and Implications for the Future
Abstract
Purpose: To review and discuss current innovations and future implications of promising biotechnology and biomedical offerings in the field of retina. We focus on therapies that have already emerged as clinical offerings or are poised to do so.
Methods: Literature review and commentary focusing on stem cell therapies, gene-based therapies, optogenetic therapies, and retinal prosthetic devices.
Results: The technologies discussed herein are some of the more recent promising biotechnology and biomedical developments within the field of retina. Retinal prosthetic devices and gene-based therapies both have an FDA-approved product for ophthalmology, and many other offerings (including optogenetics) are in the pipeline. Stem cell therapies offer personalized medicine through novel regenerative mechanisms but entail complex ethical and reimbursement challenges.
Conclusion: Stem cell therapies, gene-based therapies, optogenetics, and retinal prosthetic devices represent a new era of biotechnological and biomedical progress. These bring new ethical, regulatory, care delivery, and reimbursement challenges. By addressing these issues proactively, we may accelerate delivery of care to patients in a safe, efficient, and value-based manner.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any financial/conflicting interests to disclose.
Figures

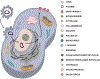

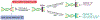
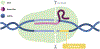

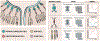
Similar articles
-
[Optogenetics and prosthetic treatment of retinal degeneration].Vestn Oftalmol. 2015 May-Jun;131(3):99-111. doi: 10.17116/oftalma2015131399-111. Vestn Oftalmol. 2015. PMID: 26310015 Review. Russian.
-
Retinal prosthetics, optogenetics, and chemical photoswitches.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Oct 15;5(10):895-901. doi: 10.1021/cn5001233. Epub 2014 Aug 8. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25089879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging therapies for inherited retinal degeneration.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Dec 7;8(368):368rv6. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf2838. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27928030 Review.
-
Prospects of Optogenetic Prosthesis of the Degenerative Retina of the Eye.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019 May;84(5):479-490. doi: 10.1134/S0006297919050031. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019. PMID: 31234763 Review.
-
Optogenetic Therapy for Visual Restoration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 30;23(23):15041. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315041. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Therapy to the Retina and the Cochlea.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 17;15:652215. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.652215. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33815052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology in regenerative ophthalmology.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Aug;148:290-307. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019. PMID: 31707052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the role of EYS in retinal degeneration: clinical and molecular aspects and its implications for future therapy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 May 17;16(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-01843-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34001227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A method to construct key success factors in the cell therapy industry.Sci Prog. 2021 Sep;104(3_suppl):368504211055640. doi: 10.1177/00368504211055640. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 34758662 Free PMC article.
-
Smart polymers for cell therapy and precision medicine.J Biomed Sci. 2019 Oct 18;26(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0571-4. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 31623607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998; 282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

