MicroRNA‑3653 inhibits the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting ITGB1
- PMID: 30664185
- PMCID: PMC6365710
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2019.6971
MicroRNA‑3653 inhibits the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting ITGB1
Abstract
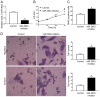
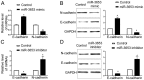
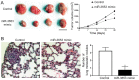
microRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the expression and biological function of miR‑3653 in HCC remain unknown. The present study demonstrated that miR‑3653 expression was significantly decreased in HCC tissues and cells using qRT‑PCR. A decreased miR‑3653 level was associated with unfavorable clinical features and poor prognosis of HCC patients. MTT, BrdU, Transwell and western blot assays showed that miR‑3653 overexpression inhibited the growth, migration, invasion and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) of HCCLM3 cells while its knockdown promoted the growth and metastatic ability of Hep3B cells. In vivo experiments showed that miR‑3653 overexpression inhibited the subcutaneous and the lung metastasis of HCCLM3 cells in nude mice. Mechanistically, integrin‑β1 (ITGB1) was identified to be the downstream target of miR‑3653 in HCC. ITGB1 overexpression reversed the inhibitory effects of miR‑3653 on the growth, metastasis and EMT of HCCLM3 cells.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

