Wnt Pathway in Bone Repair and Regeneration - What Do We Know So Far
- PMID: 30666305
- PMCID: PMC6330281
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00170
Wnt Pathway in Bone Repair and Regeneration - What Do We Know So Far
Abstract
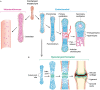
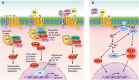
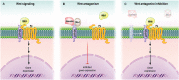
Wnt signaling plays a central regulatory role across a remarkably diverse range of functions during embryonic development, including those involved in the formation of bone and cartilage. Wnt signaling continues to play a critical role in adult osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Disruptions in this highly-conserved and complex system leads to various pathological conditions, including impaired bone healing, autoimmune diseases and malignant degeneration. For reconstructive surgeons, critically sized skeletal defects represent a major challenge. These are frequently associated with significant morbidity in both the recipient and donor sites. The Wnt pathway is an attractive therapeutic target with the potential to directly modulate stem cells responsible for skeletal tissue regeneration and promote bone growth, suggesting that Wnt factors could be used to promote bone healing after trauma. This review summarizes our current understanding of the essential role of the Wnt pathway in bone regeneration and repair.
Keywords: Wnt; bone; canonical; non-canonical; regeneration; repair; stem cells; β-catenin.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

