Very Early Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy During Acute HIV Infection Is Associated With Normalized Levels of Immune Activation Markers in Cerebrospinal Fluid but Not in Plasma
- PMID: 30668739
- PMCID: PMC6833977
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiz030
Very Early Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy During Acute HIV Infection Is Associated With Normalized Levels of Immune Activation Markers in Cerebrospinal Fluid but Not in Plasma
Abstract
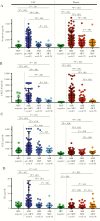
Background: Chronic immune activation in the blood and central nervous system is a consequence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection that contributes to disease morbidity and can occur despite virally suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART). The trajectory of HIV-related inflammation may vary with the timing of ART initiation. We examined immune activation markers in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood specimens collected over 96 weeks from participants who initiated ART during acute HIV infection (AHI).
Methods: RV254/SEARCH010 study participants with AHI underwent CSF (n = 89) and plasma (n = 146) sampling before initiating ART and at weeks 24 and 96 of treatment. A majority participants (64.4%) received a standard ART regimen (hereafter, "standard ART"), with some (34.7%) also receiving maraviroc and raltegravir for the first 24 weeks (hereafter, "ART plus"). We compared neopterin, CXCL10, CCL2, and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels in the AHI group to those in 18 healthy, uninfected controls.
Results: Following 24 and 96 weeks of treatment, levels of all CSF markers normalized while levels of several plasma markers remained elevated in the AHI group (P < .001). Participants receiving the ART-plus regimen had lower median plasma CCL2 levels at week 24 and lower plasma neopterin levels at week 96.
Conclusions: ART initiation during AHI differentially impacts the brain compartment, with markers of inflammation returning to normal levels in the CSF, where they were sustained at week 96, but not in plasma.
Keywords: CSF; acute HIV; immune activation; inflammation.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Antiretroviral Treatment of Acute HIV Infection Normalizes Levels of Cerebrospinal Fluid Markers of Central Nervous System (CNS) Inflammation: A Consequence of a Reduced CNS Reservoir?J Infect Dis. 2019 Nov 6;220(12):1867-1869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz031. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30668742 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ulfhammer G, Edén A, Mellgren Å, et al. . Persistent CNS immune activation following >10 years of effective HIV antiretroviral treatment. AIDS 2018 Sep 24; 32:2171–8. - PubMed

