MicroRNA-135a-3p regulates angiogenesis and tissue repair by targeting p38 signaling in endothelial cells
- PMID: 30668922
- PMCID: PMC6436660
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201802063RR
MicroRNA-135a-3p regulates angiogenesis and tissue repair by targeting p38 signaling in endothelial cells
Abstract
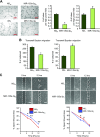
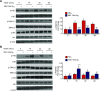
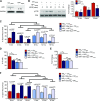
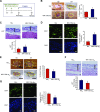
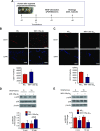
Angiogenesis is a critical process in repair of tissue injury that is regulated by a delicate balance between pro- and antiangiogenic factors. In disease states associated with impaired angiogenesis, we identified that miR-135a-3p is rapidly induced and serves as an antiangiogenic microRNA (miRNA) by targeting endothelial cell (EC) p38 signaling in vitro and in vivo. MiR-135a-3p overexpression significantly inhibited EC proliferation, migration, and network tube formation in matrigel, whereas miR-135-3p neutralization had the opposite effects. Mechanistic studies using transcriptomic profiling, bioinformatics, 3'-UTR reporter and miRNA ribonucleoprotein complex -immunoprecipitation assays, and small interfering RNA dependency studies revealed that miR-135a-3p inhibits the p38 signaling pathway in ECs by targeting huntingtin-interacting protein 1 (HIP1). Local delivery of miR-135a-3p inhibitors to wounds of diabetic db/db mice markedly increased angiogenesis, granulation tissue thickness, and wound closure rates, whereas local delivery of miR-135a-3p mimics impaired these effects. Finally, through gain- and loss-of-function studies in human skin organoids as a model of tissue injury, we demonstrated that miR-135a-3p potently modulated p38 signaling and angiogenesis in response to VEGF stimulation by targeting HIP1. These findings establish miR-135a-3p as a pivotal regulator of pathophysiological angiogenesis and tissue repair by targeting a VEGF-HIP1-p38K signaling axis, providing new targets for angiogenic therapy to promote tissue repair.-Icli, B., Wu, W., Ozdemir, D., Li, H., Haemmig, S., Liu, X., Giatsidis, G., Cheng, H. S., Avci, S. N., Kurt, M., Lee, N., Guimaraes, R. B., Manica, A., Marchini, J. F., Rynning, S. E., Risnes, I., Hollan, I., Croce, K., Orgill, D. P., Feinberg, M. W. MicroRNA-135a-3p regulates angiogenesis and tissue repair by targeting p38 signaling in endothelial cells.
Keywords: VEGF; diabetic wounds; human organoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors thank Lay-Hong Ang (Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA) for confocal microscopy technical assistance, and the Harvard Digestive Disease Center and U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant P30DK034854 This work was supported by the NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Grants HL115141, HL117994, and HL134849, and NIH National Institute of General Medical Sciences Grant GM115605 (to M.W.F.); the Arthur K. Watson Charitable Trust (to M.W.F.); the Dr. Ralph and Marian Falk Medical Research Trust (Bank of America, N.A., Trustee; to M.W.F.); the American Heart Association Grant 18SFRN33900144 (to M.W.F.); the American Diabetes Association Grant 1-16-JDF-046 (to B.I.); the Watkins Discovery Award (to B.I.); the Lerner Young Investigator Award (to B.I.); a Tübitak Predoctoral Scholarship (to D.O.); and a grant from South-Eastern Regional Health Authorities and from Norwegian Women’s Public Health Association, Norway (to I.H.). The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Falanga V. (2005) Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet 366, 1736–1743 - PubMed
-
- Potente M., Gerhardt H., Carmeliet P. (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146, 873–887 - PubMed
-
- Kusumanto Y. H., van Weel V., Mulder N. H., Smit A. J., van den Dungen J. J., Hooymans J. M., Sluiter W. J., Tio R. A., Quax P. H., Gans R. O., Dullaart R. P., Hospers G. A. (2006) Treatment with intramuscular vascular endothelial growth factor gene compared with placebo for patients with diabetes mellitus and critical limb ischemia: a double-blind randomized trial. Hum. Gene Ther. 17, 683–691 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

