Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Cell⁻Cell Communication in the Nervous System: Focus on Neurological Diseases
- PMID: 30669512
- PMCID: PMC6359416
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020434
Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Cell⁻Cell Communication in the Nervous System: Focus on Neurological Diseases
Abstract
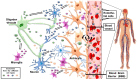
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, are membranous particles released by cells into the extracellular space. They are involved in cell differentiation, tissue homeostasis, and organ remodelling in virtually all tissues, including the central nervous system (CNS). They are secreted by a range of cell types and via blood reaching other cells whose functioning they can modify because they transport and deliver active molecules, such as proteins of various types and functions, lipids, DNA, and miRNAs. Since they are relatively easy to isolate, exosomes can be characterized, and their composition elucidated and manipulated by bioengineering techniques. Consequently, exosomes appear as promising theranostics elements, applicable to accurately diagnosing pathological conditions, and assessing prognosis and response to treatment in a variety of disorders. Likewise, the characteristics and manageability of exosomes make them potential candidates for delivering selected molecules, e.g., therapeutic drugs, to specific target tissues. All these possible applications are pertinent to research in neurophysiology, as well as to the study of neurological disorders, including CNS tumors, and autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases. In this brief review, we discuss what is known about the role and potential future applications of exosomes in the nervous system and its diseases, focusing on cell⁻cell communication in physiology and pathology.
Keywords: biomarkers; cell–cell interaction; central nervous system; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; nervous system; neurological diseases; theranostics tools.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
On the Choice of the Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Purposes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 9;20(2):236. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020236. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30634425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence-Based Clinical Use of Nanoscale Extracellular Vesicles in Nanomedicine.ACS Nano. 2016 Apr 26;10(4):3886-99. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b08015. Epub 2016 Mar 15. ACS Nano. 2016. PMID: 26978483 Review.
-
The Role of Exosomes/Extracellular Vesicles in Neural Signal Transduction.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(8):1119-1125. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00167. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 30068858 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Theranostics.Theranostics. 2017 Sep 26;7(17):4168-4182. doi: 10.7150/thno.21274. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29158817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intercellular communication by extracellular vesicles and their microRNAs in asthma.Clin Ther. 2014 Jun 1;36(6):873-81. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Clin Ther. 2014. PMID: 24909737
Cited by
-
Targeting exosomal double-stranded RNA-TLR3 signaling pathway attenuates morphine tolerance and hyperalgesia.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Oct 15;5(10):101782. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101782. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39413734 Free PMC article.
-
COMBSecretomics: A pragmatic methodological framework for higher-order drug combination analysis using secretomics.PLoS One. 2020 May 14;15(5):e0232989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232989. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32407402 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Regeneration and Rehabilitation Recovery after Stroke.Biology (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;10(9):843. doi: 10.3390/biology10090843. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles, Stem Cells and the Role of miRNAs in Neurodegeneration.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(8):1450-1478. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210817150141. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34414870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Individuals with Down Syndrome Propagate Tau Pathology in the Wildtype Mouse Brain.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 31;10(17):3931. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173931. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34501378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fais S., O’Driscoll L., Borras F.E., Buzas E., Camussi G., Cappello F., Carvalho J., Cordeiro da Silva A., Del Portillo H., El Andaloussi S., et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Use of Nanoscale Extracellular Vesicles in Nanomedicine. ACS Nano. 2016;10:3886–3899. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b08015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

