Creative Arts Interventions to Address Depression in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Outcomes, Processes, and Mechanisms
- PMID: 30671000
- PMCID: PMC6331422
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02655
Creative Arts Interventions to Address Depression in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Outcomes, Processes, and Mechanisms
Abstract
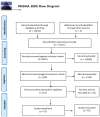
Depression experienced by older adults is proving an increasing global health burden, with rates generally 7% and as high as 27% in the USA. This is likely to significantly increase in coming years as the number and proportion of older adults in the population rises all around the world. Therefore, it is imperative that the effectiveness of approaches to the prevention and treatment of depression are understood. Creative arts interventions, including art, dance movement, drama, and music modalities, are utilized internationally to target depression and depressive symptoms in older adults. This includes interventions led by trained arts therapists as well as other health and arts professionals. However, to date there has not been a systematic review that reports effects and examines the processes (why) and mechanisms (how) of creative arts interventions are used to address depression in this older age group. This systematic review of studies on creative arts interventions for older adults experiencing depression examined: outcomes of four creative arts modalities (art, dance movement, drama, and music); with particular attention paid to processes documented as contributing to change in each modality; and mechanisms considered to result from these processes. Our analysis of 75 articles (17 art, 13 dance, 4 drama, and 41 music) indicates mostly significant quantitative or positive qualitative findings, particularly for interventions led by creative arts therapists. Mechanisms of change gleaned from the studies that were common across modalities include physical (e.g., increased muscle strength; neurochemical effects, such as endorphin release), intra-personal (e.g., enhanced self-concept, strengthened agency and mastery; processing and communication of emotions), cultural (e.g., creative expression, aesthetic pleasure), cognitive (e.g., stimulation of memory), and social (e.g., increased social skills and connection), that were all considered to contribute to reduced depression and symptoms. Recommendations for future research includes stronger focus on testing of processes and mechanisms.
Keywords: arts therapy; creative arts therapy; dance movement therapy; depression; drama therapy; older adults; outcomes; processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An integrative systematic review of creative arts interventions for older informal caregivers of people with neurological conditions.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 7;15(12):e0243461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243461. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33284840 Free PMC article.
-
Creative Arts Interventions for Stress Management and Prevention-A Systematic Review.Behav Sci (Basel). 2018 Feb 22;8(2):28. doi: 10.3390/bs8020028. Behav Sci (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29470435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness and mechanisms of the arts therapies in forensic care. A systematic review, narrative synthesis, and meta analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2023 May 19;14:1128252. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1128252. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37275972 Free PMC article.
-
How the arts heal: a review of the neural mechanisms behind the therapeutic effects of creative arts on mental and physical health.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Oct 2;18:1422361. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1422361. eCollection 2024. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39416439 Free PMC article.
-
Colors of the mind: a meta-analysis of creative arts therapy as an approach for post-traumatic stress disorder intervention.BMC Psychol. 2025 Jan 12;13(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02361-4. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39799380 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systematic review of social prescribing and older adults: where to from here?Fam Med Community Health. 2022 Oct;10(Suppl 1):e001829. doi: 10.1136/fmch-2022-001829. Fam Med Community Health. 2022. PMID: 36207017 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends in drama therapy: a bibliometric analysis based on Scopus.Front Psychol. 2023 Dec 21;14:1327656. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1327656. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38179487 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Waitlist-Controlled Trial of an Intergenerational Arts and Heritage-Based Intervention in Singapore: Project ARTISAN.Front Psychol. 2021 Sep 6;12:730709. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.730709. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34552538 Free PMC article.
-
Meeting the multidimensional self: fostering selfhood at the interface of Creative Arts Therapies and neuroscience.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1417035. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1417035. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39386142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Death Education for Palliative Psychology: The Impact of a Death Education Course for Italian University Students.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;13(2):182. doi: 10.3390/bs13020182. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam D., Shahar S., Ramli A. (2016b). Status of functional balance and anxiety level among cognitive impaired elderly underwent dance and relaxation therapy. Inter. Med. J. 23, 686–690.
-
- Ahessy B. (2013). Creative Arts Therapies: what psychologists need to know. Irish Psychol. 1, 274–281.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous