Protein Disulfide Isomerase Modulates the Activation of Thyroid Hormone Receptors
- PMID: 30671024
- PMCID: PMC6331412
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00784
Protein Disulfide Isomerase Modulates the Activation of Thyroid Hormone Receptors
Abstract
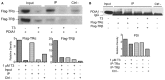
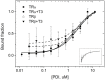
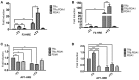
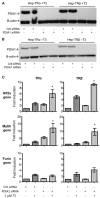
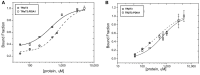
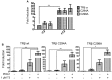
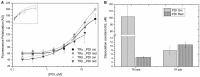
Thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) are responsible for mediating thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) actions at a cellular level. They belong to the nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily and execute their main functions inside the cell nuclei as hormone-regulated transcription factors. These receptors also exhibit so-called "non-classic" actions, for which other cellular proteins, apart from coregulators inside nuclei, regulate their activity. Aiming to find alternative pathways of TR modulation, we searched for interacting proteins and found that PDIA1 interacts with TRβ in a yeast two-hybrid screening assay. The functional implications of PDIA1-TR interactions are still unclear; however, our co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) and fluorescence assay results showed that PDI was able to bind both TR isoforms in vitro. Moreover, T3 appears to have no important role in these interactions in cellular assays, where PDIA1 was able to regulate transcription of TRα and TRβ-mediated genes in different ways depending on the promoter region and on the TR isoform involved. Although PDIA1 appears to act as a coregulator, it binds to a TR surface that does not interfere with coactivator binding. However, the TR:PDIA1 complex affinity and activation are different depending on the TR isoform. Such differences may reflect the structural organization of the PDIA1:TR complex, as shown by models depicting an interaction interface with exposed cysteines from both proteins, suggesting that PDIA1 might modulate TR by its thiol reductase/isomerase activity.
Keywords: nuclear receptor signaling pathways; protein complexes; protein disulfide isomerase; redox regulation; thyroid hormone receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the functional role of steroid receptor coactivator-1 in ligand-induced transactivation by thyroid hormone receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Jun;11(6):755-67. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.6.0003. Mol Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9171239
-
General receptor for phosphoinositides 1, a novel repressor of thyroid hormone receptor action that prevents deoxyribonucleic acid binding.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Aug;19(8):1991-2005. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0449. Epub 2005 May 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15878955
-
Lack of coactivator interaction can be a mechanism for dominant negative activity by mutant thyroid hormone receptors.Endocrinology. 1998 Oct;139(10):4197-204. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.10.6218. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9751500
-
Functions of thyroid hormone receptors in mice.Thyroid. 2000 Jan;10(1):41-52. doi: 10.1089/thy.2000.10.41. Thyroid. 2000. PMID: 10691312 Review.
-
Role of co-activators and co-repressors in the mechanism of steroid/thyroid receptor action.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:141-64; discussion 164-5. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997. PMID: 9238851 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Proteomic and Metabolomic Analysis of Human Osteoblasts, Differentiated from Dental Pulp Stem Cells, Hinted Crucial Signaling Pathways Promoting Osteogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 24;22(15):7908. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157908. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360674 Free PMC article.
-
Protein disulfide isomerase A1‑associated pathways in the development of stratified breast cancer therapies.Int J Oncol. 2022 Feb;60(2):16. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5306. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35014681 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and mechanisms of protein disulfide isomerase family in cancer emergence.Cell Biosci. 2022 Aug 14;12(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00868-6. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35965326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

